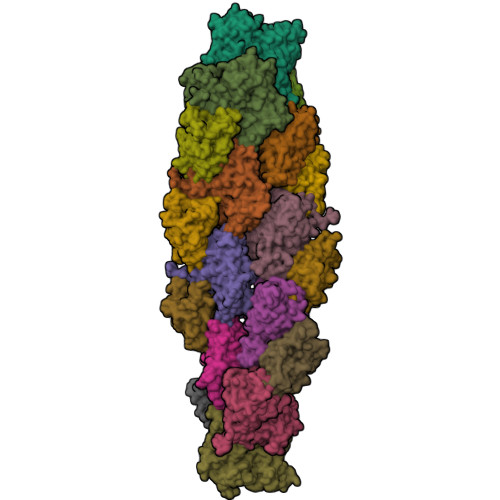
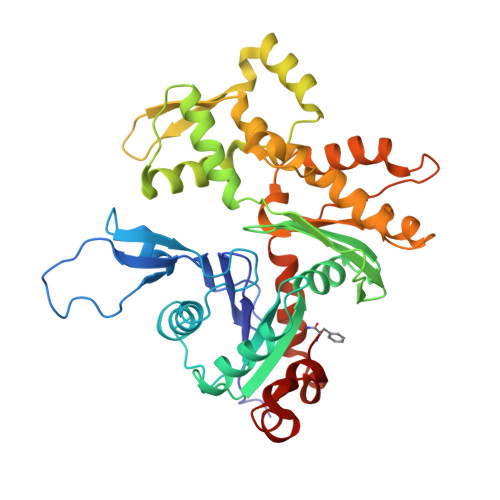
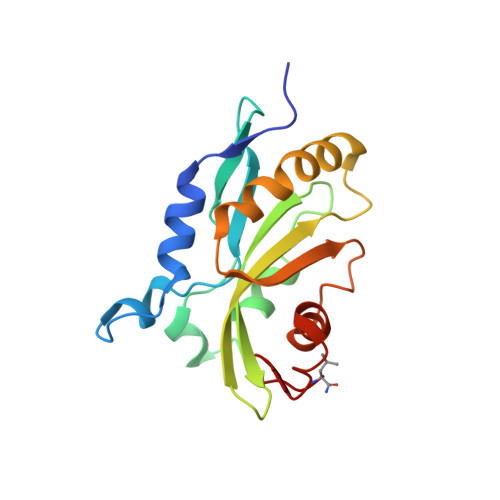
Magic angle spinning NMR structure of human cofilin-2 assembled on actin filaments reveals isoform-specific conformation and binding mode.
Kraus, J., Russell, R.W., Kudryashova, E., Xu, C., Katyal, N., Perilla, J.R., Kudryashov, D.S., Polenova, T.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 2114-2114
- PubMed: 35440100
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29595-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7M0G, 7U8K - PubMed Abstract:
Actin polymerization dynamics regulated by actin-binding proteins are essential for various cellular functions. The cofilin family of proteins are potent regulators of actin severing and filament disassembly. The structural basis for cofilin-isoform-specific severing activity is poorly understood as their high-resolution structures in complex with filamentous actin (F-actin) are lacking. Here, we present the atomic-resolution structure of the muscle-tissue-specific isoform, cofilin-2 (CFL2), assembled on ADP-F-actin, determined by magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy and data-guided molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. We observe an isoform-specific conformation for CFL2. This conformation is the result of a unique network of hydrogen bonding interactions within the α2 helix containing the non-conserved residue, Q26. Our results indicate F-site interactions that are specific between CFL2 and ADP-F-actin, revealing mechanistic insights into isoform-dependent F-actin disassembly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716, United States.