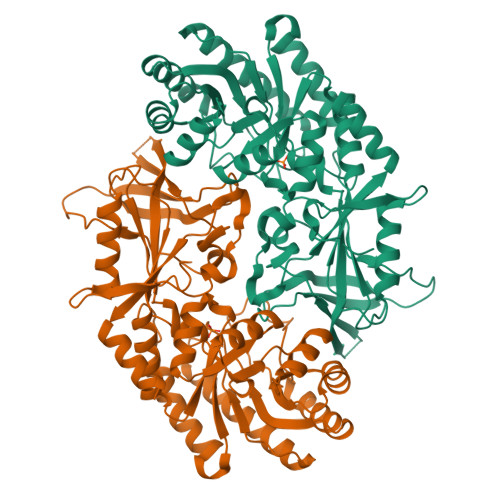
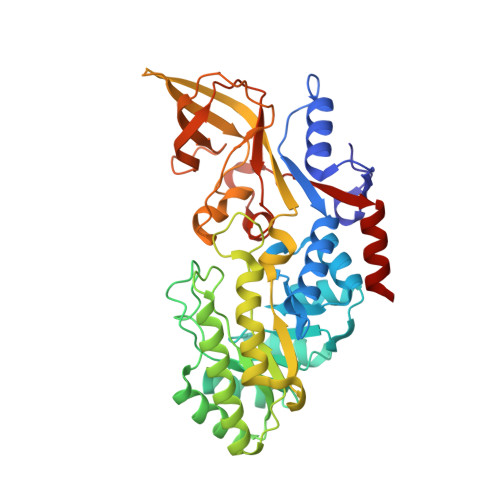
Structure and Enzymatic Activity of an Intellectual Disability-Associated Ornithine Decarboxylase Variant, G84R.
Zhou, X.E., Schultz, C.R., Suino Powell, K., Henrickson, A., Lamp, J., Brunzelle, J.S., Demeler, B., Vega, I.E., Bachmann, A.S., Melcher, K.(2022) ACS Omega 7: 34665-34675
- PubMed: 36188294
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c04702
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7U6P, 7U6U - PubMed Abstract:
Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is a rate-limiting enzyme for the synthesis of polyamines (PAs). PAs are required for proliferation, and increased ODC activity is associated with cancer and neural over-proliferation. ODC levels and activity are therefore tightly regulated, including through the ODC-specific inhibitor, antizyme AZ1. Recently, ODC G84R has been reported as a partial loss-of-function variant that is associated with intellectual disability and seizures. However, G84 is distant from both the catalytic center and the ODC homodimerization interface. To understand how G84R modulates ODC activity, we have determined the crystal structure of ODC G84R in both the presence and the absence of the cofactor pyridoxal 5-phosphate. The structures show that the replacement of G84 by arginine leads to hydrogen bond formation of R84 with F420, the last residue of the ODC C-terminal helix, a structural element that is involved in the AZ1-mediated proteasomal degradation of ODC. In contrast, the catalytic center is essentially indistinguishable from that of wildtype ODC. We therefore reanalyzed the catalytic activity of ODC G84R and found that it is rescued when the protein is purified in the presence of a reducing agent to mimic the reducing environment of the cytoplasm. This suggests that R84 may exert its neurological effects not through reducing ODC catalytic activity but through misregulation of its AZ1-mediated proteasomal degradation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, Michigan 49503, United States.