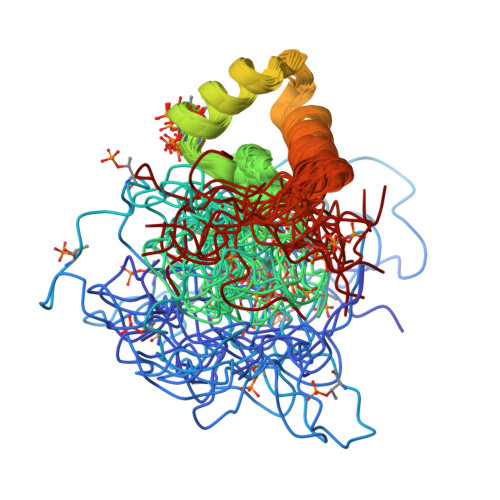
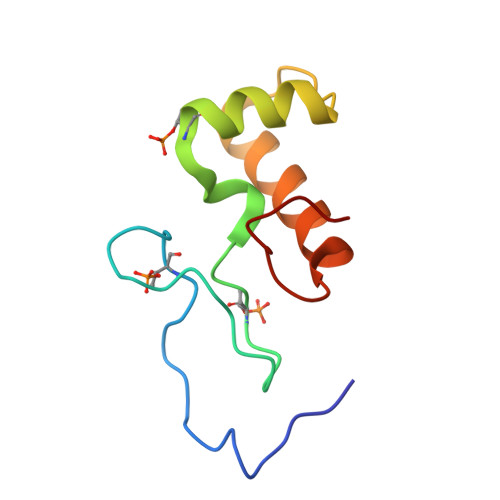
Phosphorylation of the DNA repair scaffold SLX4 drives folding of the SAP domain and activation of the MUS81-EME1 endonuclease.
Payliss, B.J., Tse, Y.W.E., Reichheld, S.E., Lemak, A., Yun, H.Y., Houliston, S., Patel, A., Arrowsmith, C.H., Sharpe, S., Wyatt, H.D.M.(2022) Cell Rep 41: 111537-111537
- PubMed: 36288699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111537
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7TUJ - PubMed Abstract:
The DNA repair scaffold SLX4 has multifaceted roles in genome stability, many of which depend on structure-selective endonucleases. SLX4 coordinates the cell cycle-regulated assembly of SLX1, MUS81-EME1, and XPF-ERCC1 into a tri-nuclease complex called SMX. Mechanistically, how the mitotic kinase CDK1 regulates the interaction between SLX4 and MUS81-EME1 remains unclear. Here, we show that CDK1-cyclin B phosphorylates SLX4 residues T1544, T1561, and T1571 in the MUS81-binding region (SLX4 MBR ). Phosphorylated SLX4 MBR relaxes the substrate specificity of MUS81-EME1 and stimulates cleavage of replication and recombination structures, providing a biochemical explanation for the chromosome pulverization that occurs when SLX4 binds MUS81 in S-phase. Remarkably, phosphorylation of SLX4 MBR drives folding of an SAP domain, which underpins the high-affinity interaction with MUS81. We also report the structure of phosphorylated SLX4 MBR and identify the MUS81-binding interface. Our work provides mechanistic insights into how cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of SLX4 drives the recruitment and activation of MUS81-EME1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON M56 1A8, Canada.