Gain-of-Signal Assays for Probing Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 M pro /3CL pro in Living Cells.
Moghadasi, S.A., Esler, M.A., Otsuka, Y., Becker, J.T., Moraes, S.N., Anderson, C.B., Chamakuri, S., Belica, C., Wick, C., Harki, D.A., Young, D.W., Scampavia, L., Spicer, T.P., Shi, K., Aihara, H., Brown, W.L., Harris, R.S.(2022) mBio 13: e0078422-e0078422
- PubMed: 35471084
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00784-22
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
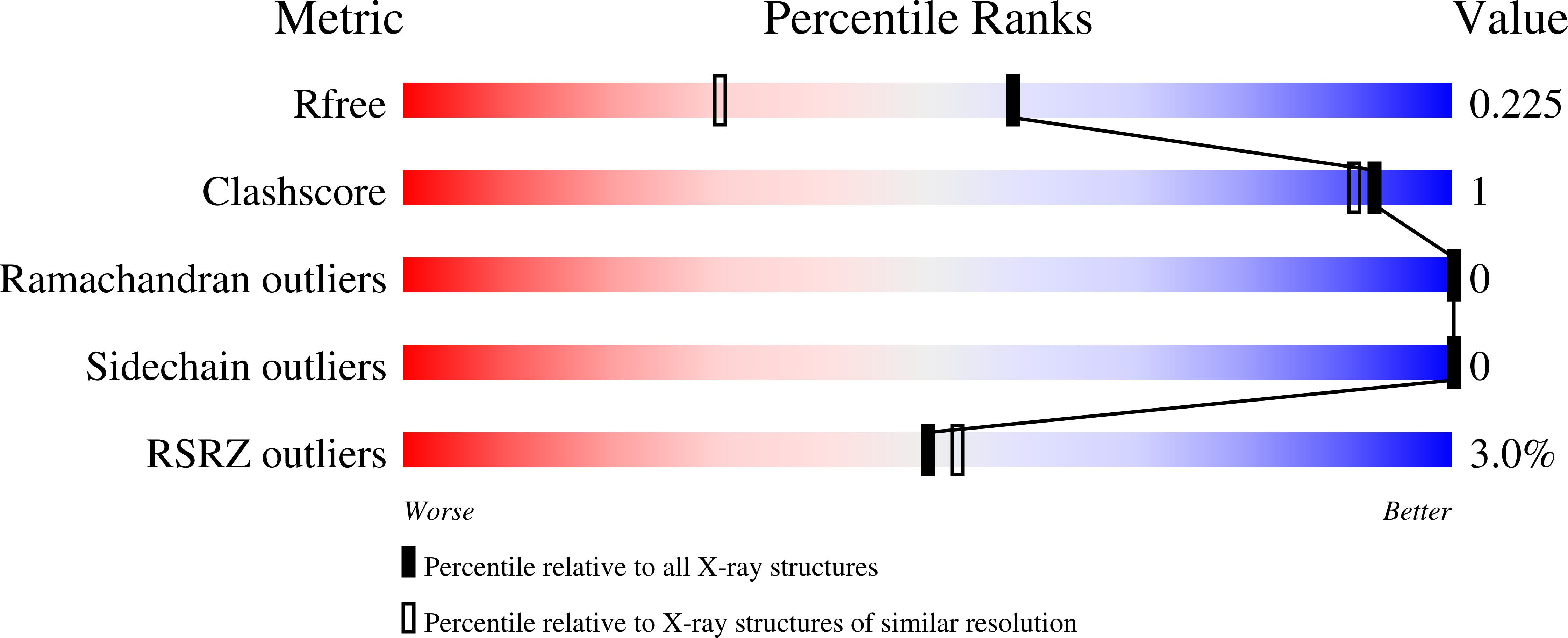
7TGR - PubMed Abstract:
The main protease, M pro , of SARS-CoV-2 is required to cleave the viral polyprotein into precise functional units for virus replication and pathogenesis. Here, we report quantitative reporters for M pro function in living cells in which protease inhibition by genetic or chemical methods results in robust signal readouts by fluorescence (enhanced green fluorescent protein [eGFP]) or bioluminescence (firefly luciferase). These gain-of-signal systems are scalable to high-throughput platforms for quantitative discrimination between M pro mutants and/or inhibitor potencies as evidenced by validation of several reported inhibitors. Additional utility is shown by single M pro amino acid variants and structural information combining to demonstrate that both inhibitor conformational dynamics and amino acid differences are able to influence inhibitor potency. We further show that a recent variant of concern (Omicron) has an unchanged response to a clinically approved drug, nirmatrelvir, whereas proteases from divergent coronavirus species show differential susceptibility. Together, we demonstrate that these gain-of-signal systems serve as robust, facile, and scalable assays for live cell quantification of M pro inhibition, which will help expedite the development of next-generation antivirals and enable the rapid testing of emerging variants. IMPORTANCE The main protease, M pro , of SARS-CoV-2 is an essential viral protein required for the earliest steps of infection. It is therefore an attractive target for antiviral drug development. Here, we report the development and implementation of two complementary cell-based systems for quantification of M pro inhibition by genetic or chemical approaches. The first is fluorescence based (eGFP), and the second is luminescence based (firefly luciferase). Importantly, both systems rely upon gain-of-signal readouts such that stronger inhibitors yield higher fluorescent or luminescent signal. The high versatility and utility of these systems are demonstrated by characterizing M pro mutants and natural variants, including Omicron, as well as a panel of existing inhibitors. These systems rapidly, safely, and sensitively identify M pro variants with altered susceptibilities to inhibition, triage-nonspecific, or off-target molecules and validate bona fide inhibitors, with the most potent thus far being the first-in-class drug nirmatrelvir.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesotagrid.17635.36, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA.