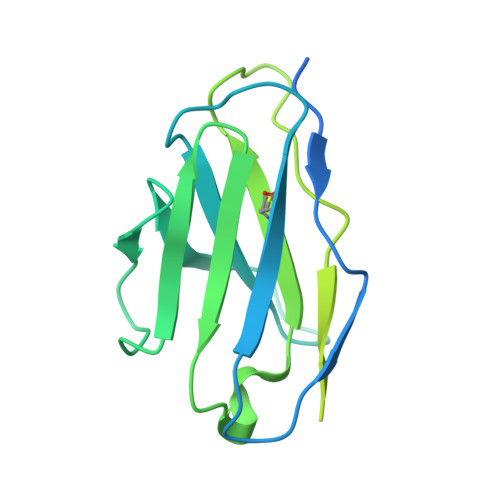
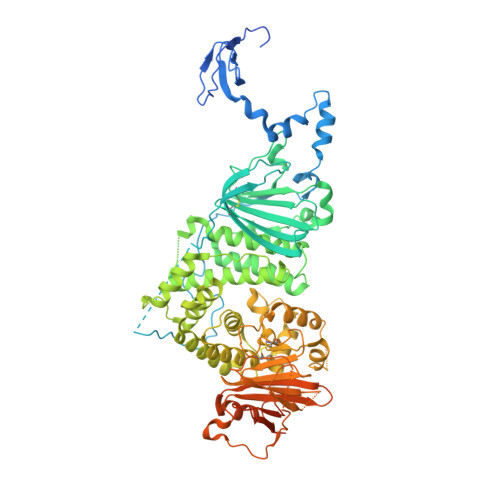
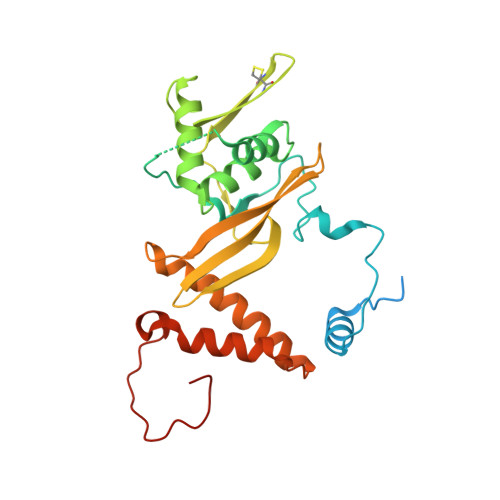
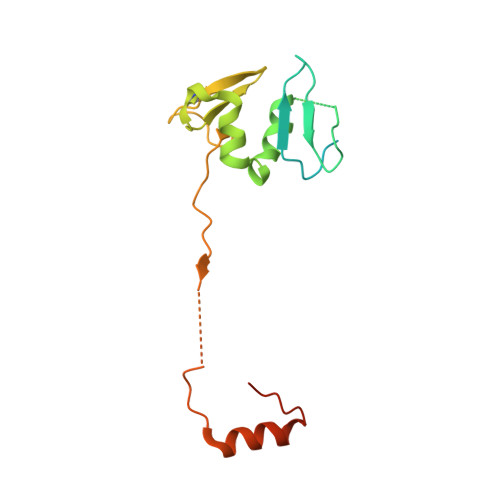
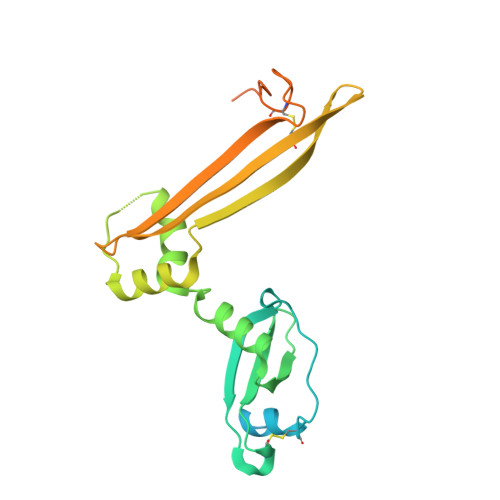
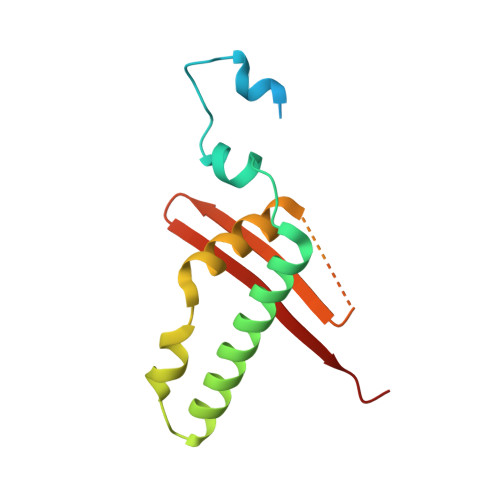
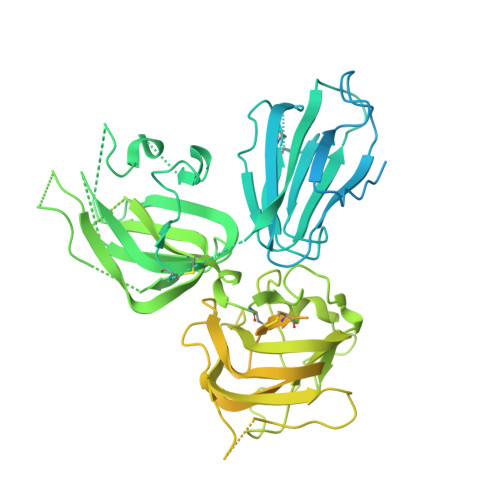
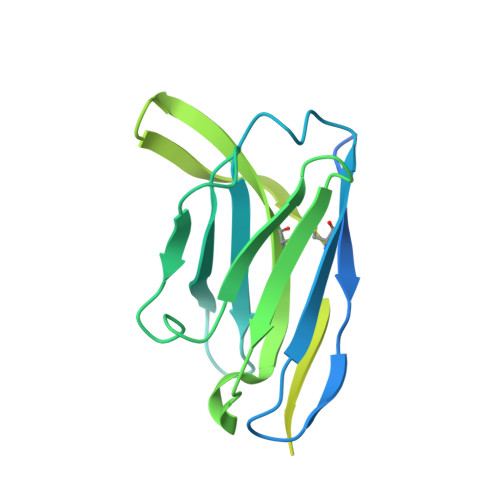
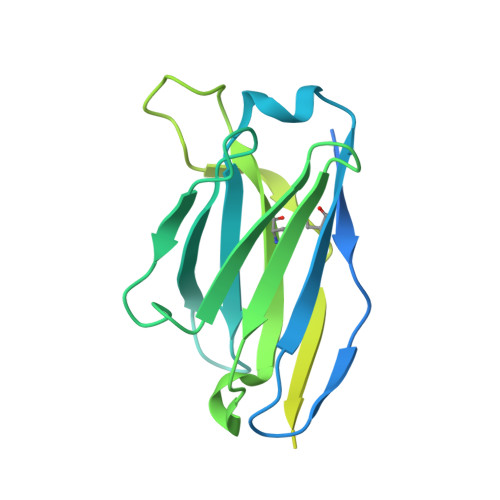
Structural basis for HCMV Pentamer receptor recognition and antibody neutralization.
Kschonsak, M., Johnson, M.C., Schelling, R., Green, E.M., Rouge, L., Ho, H., Patel, N., Kilic, C., Kraft, E., Arthur, C.P., Rohou, A.L., Comps-Agrar, L., Martinez-Martin, N., Perez, L., Payandeh, J., Ciferri, C.(2022) Sci Adv 8: eabm2536-eabm2536
- PubMed: 35275719
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abm2536
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7T4Q, 7T4R, 7T4S - PubMed Abstract:
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) represents the viral leading cause of congenital birth defects and uses the gH/gL/UL128-130-131A complex (Pentamer) to enter different cell types, including epithelial and endothelial cells. Upon infection, Pentamer elicits the most potent neutralizing response against HCMV, representing a key vaccine candidate. Despite its relevance, the structural basis for Pentamer receptor recognition and antibody neutralization is largely unknown. Here, we determine the structures of Pentamer bound to neuropilin 2 (NRP2) and a set of potent neutralizing antibodies against HCMV. Moreover, we identify thrombomodulin (THBD) as a functional HCMV receptor and determine the structures of the Pentamer-THBD complex. Unexpectedly, both NRP2 and THBD also promote dimerization of Pentamer. Our results provide a framework for understanding HCMV receptor engagement, cell entry, antibody neutralization, and outline strategies for antiviral therapies against HCMV.
- Department of Structural Biology, Genentech Inc., South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: