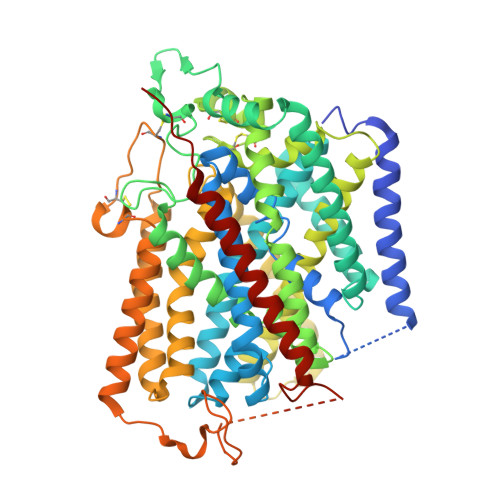
Structure and mechanism of the SGLT family of glucose transporters.
Han, L., Qu, Q., Aydin, D., Panova, O., Robertson, M.J., Xu, Y., Dror, R.O., Skiniotis, G., Feng, L.(2022) Nature 601: 274-279
- PubMed: 34880492
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04211-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SL8, 7SL9, 7SLA - PubMed Abstract:
Glucose is a primary energy source in living cells. The discovery in 1960s that a sodium gradient powers the active uptake of glucose in the intestine 1 heralded the concept of a secondary active transporter that can catalyse the movement of a substrate against an electrochemical gradient by harnessing energy from another coupled substrate. Subsequently, coupled Na + /glucose transport was found to be mediated by sodium-glucose cotransporters 2,3 (SGLTs). SGLTs are responsible for active glucose and galactose absorption in the intestine and for glucose reabsorption in the kidney 4 , and are targeted by multiple drugs to treat diabetes 5 . Several members within the SGLT family transport key metabolites other than glucose 2 . Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the prototypic human SGLT1 and a related monocarboxylate transporter SMCT1 from the same family. The structures, together with molecular dynamics simulations and functional studies, define the architecture of SGLTs, uncover the mechanism of substrate binding and selectivity, and shed light on water permeability of SGLT1. These results provide insights into the multifaceted functions of SGLTs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA, USA.