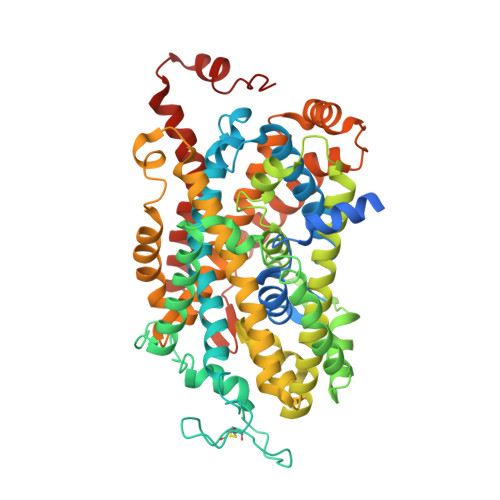
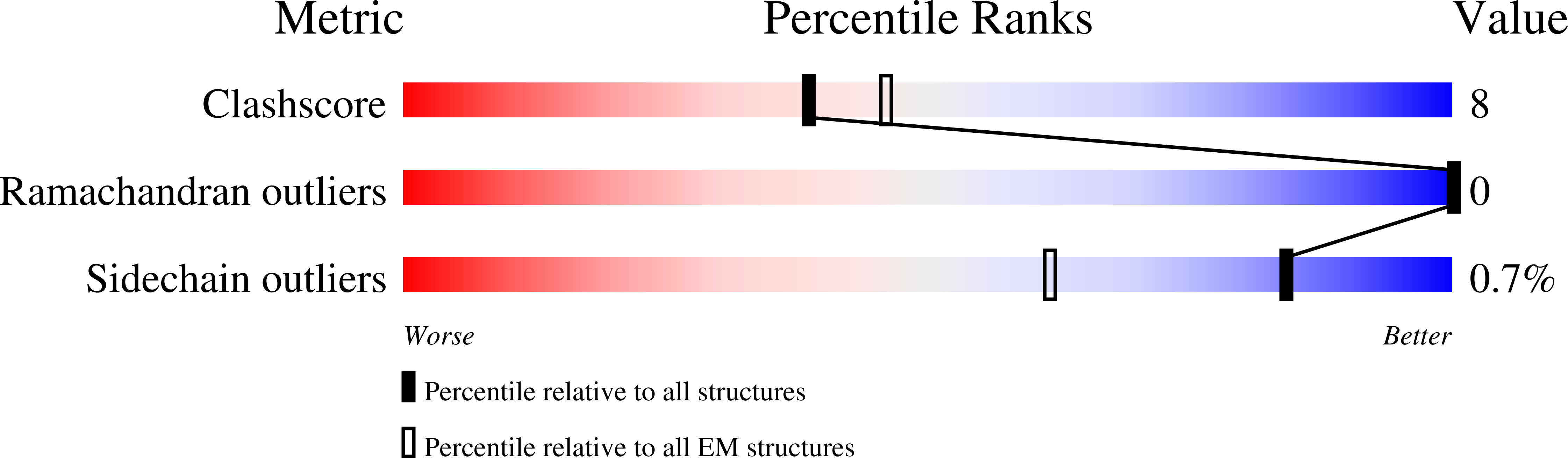Structural basis of GABA reuptake inhibition.
Motiwala, Z., Aduri, N.G., Shaye, H., Han, G.W., Lam, J.H., Katritch, V., Cherezov, V., Gati, C.(2022) Nature 606: 820-826
- PubMed: 35676483
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04814-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SK2 - PubMed Abstract:
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporter 1 (GAT1) 1 regulates neuronal excitation of the central nervous system by clearing the synaptic cleft of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA upon its release from synaptic vesicles. Elevating the levels of GABA in the synaptic cleft, by inhibiting GABA reuptake transporters, is an established strategy to treat neurological disorders, such as epilepsy 2 . Here we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length, wild-type human GAT1 in complex with its clinically used inhibitor tiagabine 3 , with an ordered part of only 60 kDa. Our structure reveals that tiagabine locks GAT1 in the inward-open conformation, by blocking the intracellular gate of the GABA release pathway, and thus suppresses neurotransmitter uptake. Our results provide insights into the mixed-type inhibition of GAT1 by tiagabine, which is an important anticonvulsant medication. Its pharmacodynamic profile, confirmed by our experimental data, suggests initial binding of tiagabine to the substrate-binding site in the outward-open conformation, whereas our structure presents the drug stalling the transporter in the inward-open conformation, consistent with a two-step mechanism of inhibition 4 . The presented structure of GAT1 gives crucial insights into the biology and pharmacology of this important neurotransmitter transporter and provides blueprints for the rational design of neuromodulators, as well as moving the boundaries of what is considered possible in single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of challenging membrane proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Bridge Institute, USC Michelson Center for Convergent Biosciences, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.