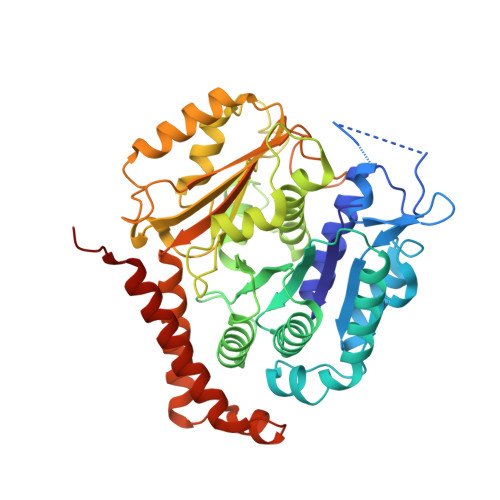
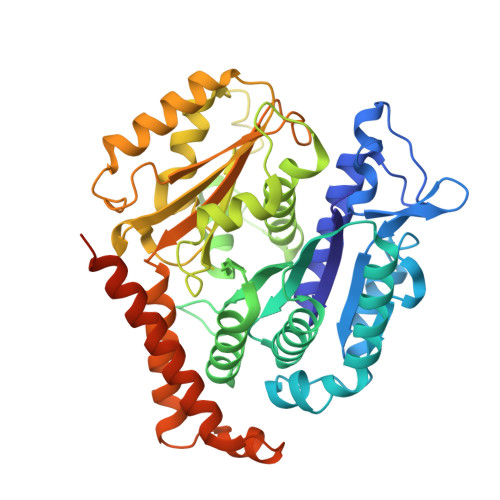
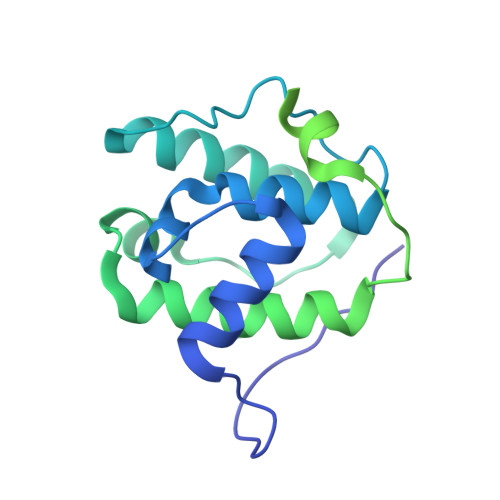
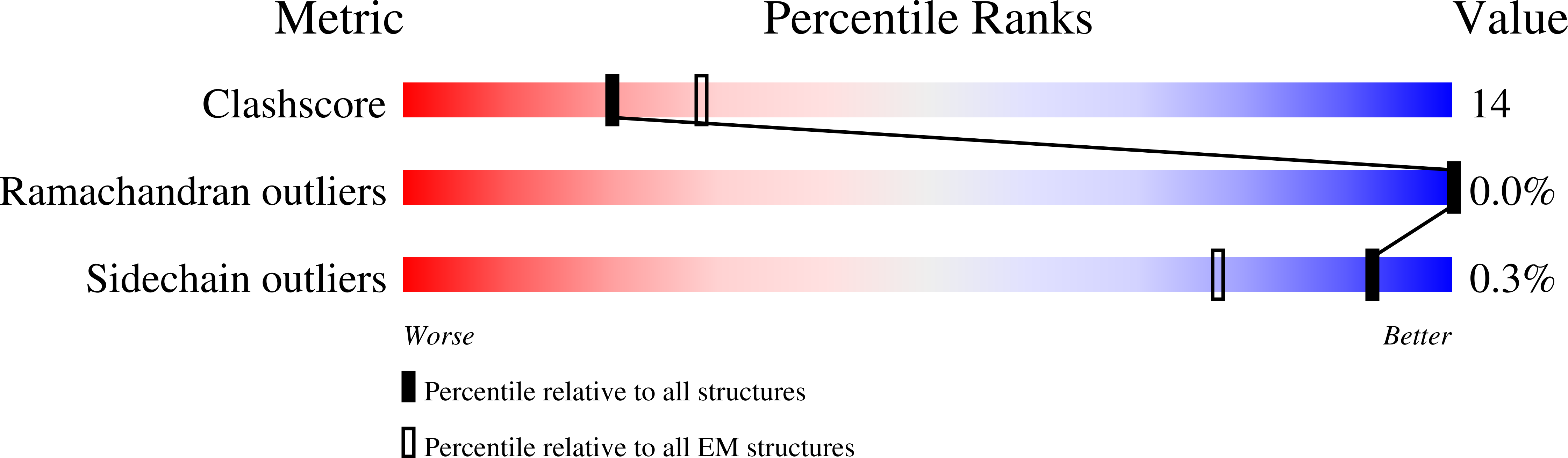Structural transitions in the GTP cap visualized by cryo-electron microscopy of catalytically inactive microtubules.
LaFrance, B.J., Roostalu, J., Henkin, G., Greber, B.J., Zhang, R., Normanno, D., McCollum, C.O., Surrey, T., Nogales, E.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119
- PubMed: 34996871
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2114994119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7SJ7, 7SJ8, 7SJ9, 7SJA - PubMed Abstract:
Microtubules (MTs) are polymers of αβ-tubulin heterodimers that stochastically switch between growth and shrinkage phases. This dynamic instability is critically important for MT function. It is believed that GTP hydrolysis within the MT lattice is accompanied by destabilizing conformational changes and that MT stability depends on a transiently existing GTP cap at the growing MT end. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy and total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy of GTP hydrolysis-deficient MTs assembled from mutant recombinant human tubulin to investigate the structure of a GTP-bound MT lattice. We find that the GTP-MT lattice of two mutants in which the catalytically active glutamate in α-tubulin was substituted by inactive amino acids (E254A and E254N) is remarkably plastic. Undecorated E254A and E254N MTs with 13 protofilaments both have an expanded lattice but display opposite protofilament twists, making these lattices distinct from the compacted lattice of wild-type GDP-MTs. End-binding proteins of the EB family have the ability to compact both mutant GTP lattices and to stabilize a negative twist, suggesting that they promote this transition also in the GTP cap of wild-type MTs, thereby contributing to the maturation of the MT structure. We also find that the MT seam appears to be stabilized in mutant GTP-MTs and destabilized in GDP-MTs, supporting the proposal that the seam plays an important role in MT stability. Together, these structures of catalytically inactive MTs add mechanistic insight into the GTP state of MTs, the stability of the GTP- and GDP-bound lattice, and our overall understanding of MT dynamic instability.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720.