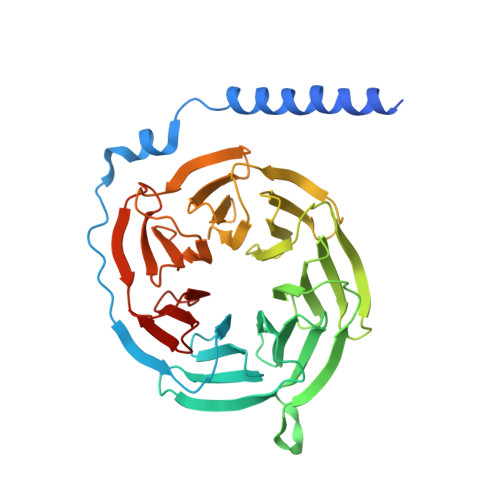
Structure, function and pharmacology of human itch GPCRs.
Cao, C., Kang, H.J., Singh, I., Chen, H., Zhang, C., Ye, W., Hayes, B.W., Liu, J., Gumpper, R.H., Bender, B.J., Slocum, S.T., Krumm, B.E., Lansu, K., McCorvy, J.D., Kroeze, W.K., English, J.G., DiBerto, J.F., Olsen, R.H.J., Huang, X.P., Zhang, S., Liu, Y., Kim, K., Karpiak, J., Jan, L.Y., Abraham, S.N., Jin, J., Shoichet, B.K., Fay, J.F., Roth, B.L.(2021) Nature 600: 170-175
- PubMed: 34789874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04126-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7S8L, 7S8M, 7S8N, 7S8O, 7S8P - PubMed Abstract:
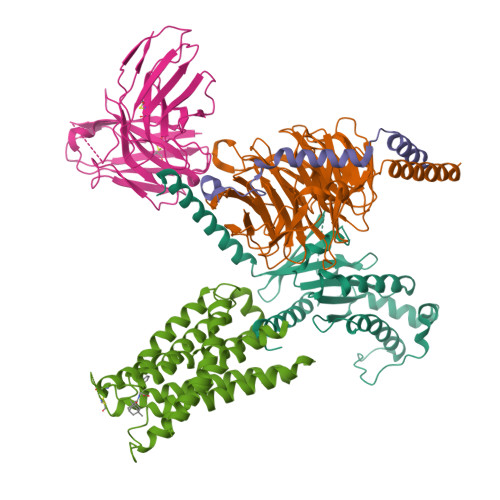
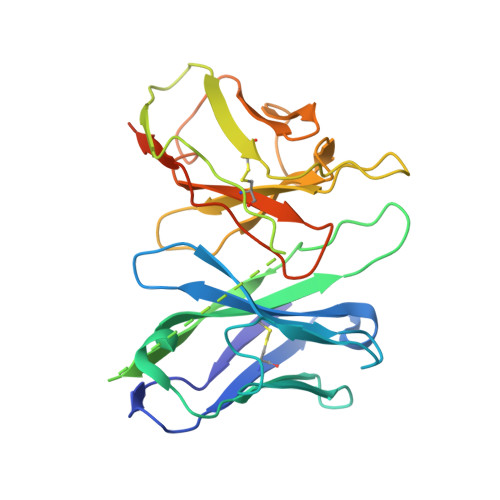
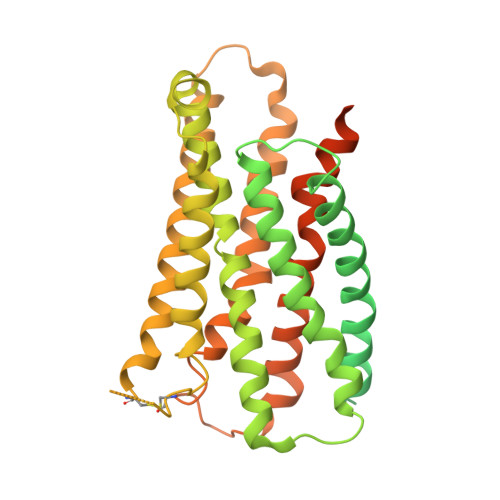
The MRGPRX family of receptors (MRGPRX1-4) is a family of mas-related G-protein-coupled receptors that have evolved relatively recently 1 . Of these, MRGPRX2 and MRGPRX4 are key physiological and pathological mediators of itch and related mast cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions 2-5 . MRGPRX2 couples to both G i and G q in mast cells 6 . Here we describe agonist-stabilized structures of MRGPRX2 coupled to G i1 and G q in ternary complexes with the endogenous peptide cortistatin-14 and with a synthetic agonist probe, respectively, and the development of potent antagonist probes for MRGPRX2. We also describe a specific MRGPRX4 agonist and the structure of this agonist in a complex with MRGPRX4 and G q . Together, these findings should accelerate the structure-guided discovery of therapeutic agents for pain, itch and mast cell-mediated hypersensitivity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.