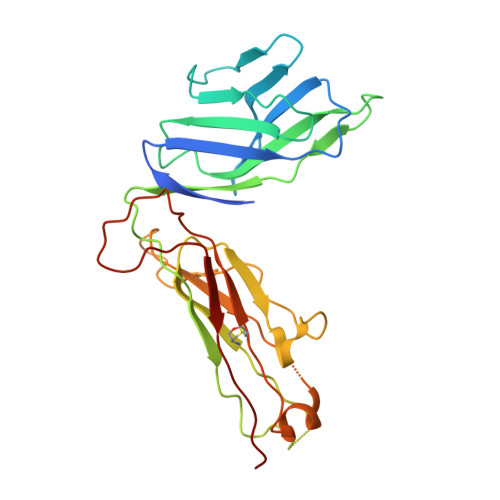
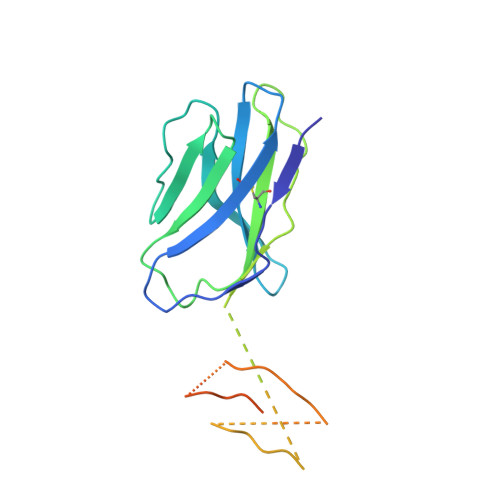
Atypical sideways recognition of CD1a by autoreactive gamma delta T cell receptors.
Wegrecki, M., Ocampo, T.A., Gunasinghe, S.D., von Borstel, A., Tin, S.Y., Reijneveld, J.F., Cao, T.P., Gully, B.S., Le Nours, J., Moody, D.B., Van Rhijn, I., Rossjohn, J.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 3872-3872
- PubMed: 35790773
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31443-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7RYL, 7RYM, 7RYN, 7RYO - PubMed Abstract:
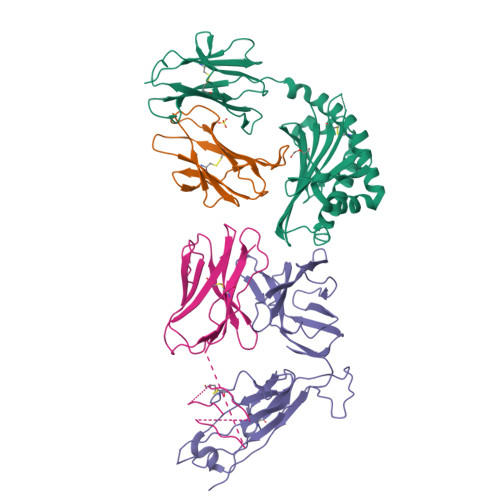
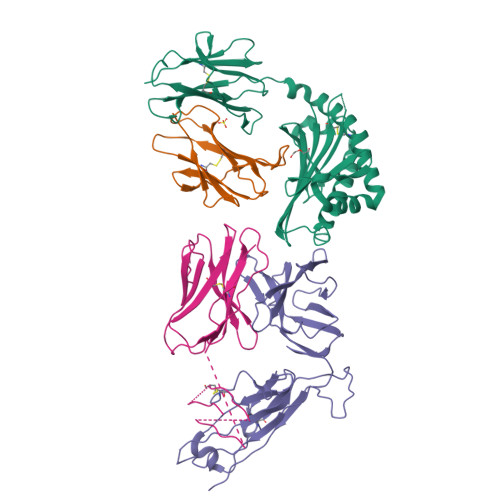
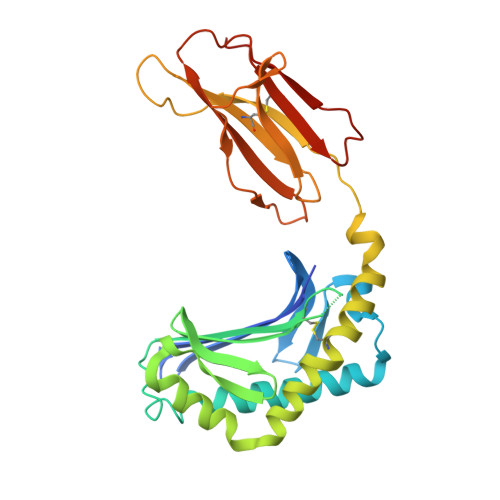
CD1a is a monomorphic antigen-presenting molecule on dendritic cells that presents lipids to αβ T cells. Whether CD1a represents a ligand for other immune receptors remains unknown. Here we use CD1a tetramers to show that CD1a is a ligand for Vδ1 + γδ T cells. Functional studies suggest that two γδ T cell receptors (TCRs) bound CD1a in a lipid-independent manner. The crystal structures of three Vγ4Vδ1 TCR-CD1a-lipid complexes reveal that the γδ TCR binds at the extreme far side and parallel to the long axis of the β-sheet floor of CD1a's antigen-binding cleft. Here, the γδ TCR co-recognises the CD1a heavy chain and β2 microglobulin in a manner that is distinct from all other previously observed γδ TCR docking modalities. The 'sideways' and lipid antigen independent mode of autoreactive CD1a recognition induces TCR clustering on the cell surface and proximal T cell signalling as measured by CD3ζ phosphorylation. In contrast with the 'end to end' binding of αβ TCRs that typically contact carried antigens, autoreactive γδ TCRs support geometrically diverse approaches to CD1a, as well as antigen independent recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Infection and Immunity Program and Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia.