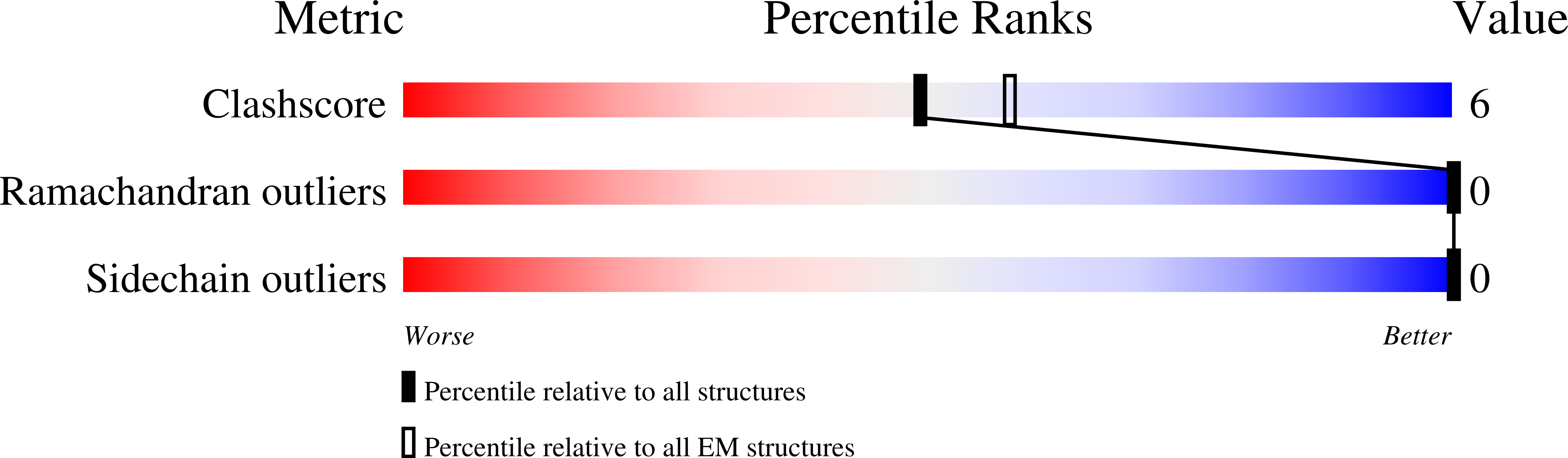Structural mechanisms of assembly, permeation, gating, and pharmacology of native human rod CNG channel.
Xue, J., Han, Y., Zeng, W., Jiang, Y.(2022) Neuron 110: 86-95.e5
- PubMed: 34699778
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.10.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7RH9, 7RHG, 7RHH, 7RHI, 7RHJ, 7RHK, 7RHL - PubMed Abstract:
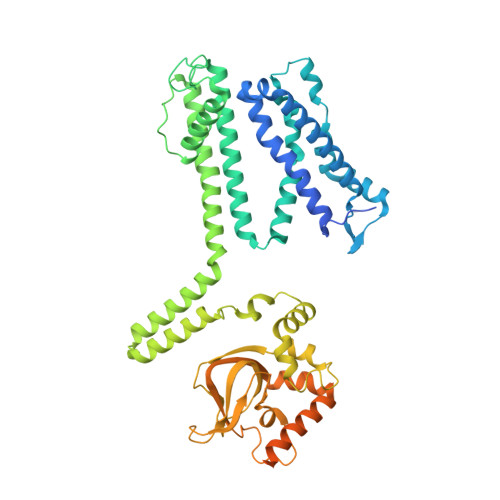
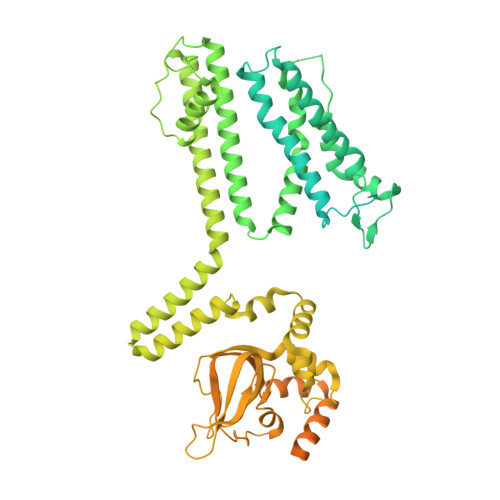
Mammalian cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels are nonselective cation channels activated by cGMP or cAMP and play essential roles in the signal transduction of the visual and olfactory sensory systems. CNGA1, the principal component of the CNG channel from rod photoreceptors, can by itself form a functional homotetrameric channel and has been used as the model system in the majority of rod CNG studies. However, the native rod CNG functions as a heterotetramer consisting of three A1 and one B1 subunits and exhibits different functional properties than the CNGA1 homomer. Here we present the functional analysis of human rod CNGA1/B1 heterotetramer and its cryo-EM structures in apo, cGMP-bound, cAMP-bound, and L-cis-Diltiazem-blocked states. These structures, with resolution ranging from 2.6 to 3.3 Å, elucidate the structural mechanisms underlying the 3:1 subunit stoichiometry, the asymmetrical gating upon cGMP activation, and the unique pharmacological property of the native rod CNG channel.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Physiology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA; Department of Biophysics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.