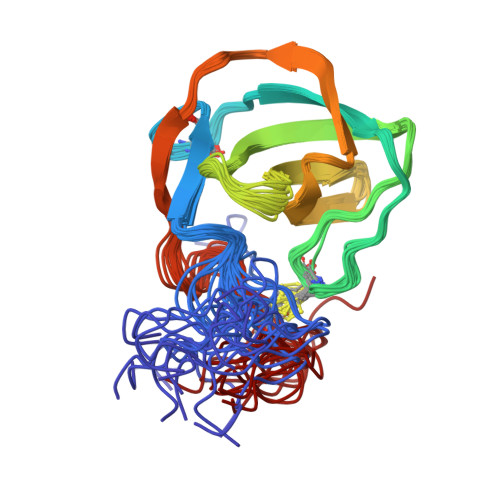
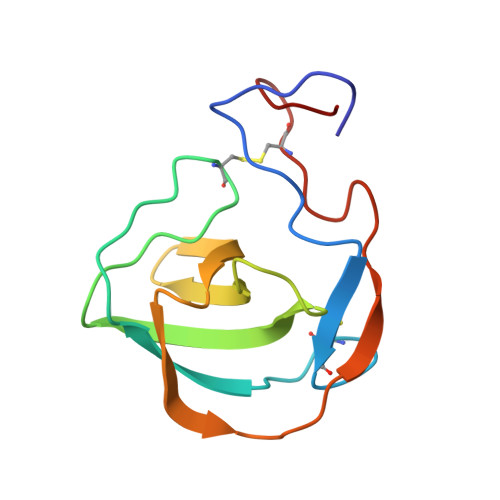
Characterization of a fold in TANGO1 evolved from SH3 domains for the export of bulky cargos.
Arnolds, O., Stoll, R.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 2273-2273
- PubMed: 37080980
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37705-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7R3M - PubMed Abstract:
Bulky cargos like procollagens, apolipoproteins, and mucins exceed the size of conventional COPII vesicles. During evolution a process emerged in metazoans, predominantly governed by the TANGO1 protein family, that organizes cargo at the exit sites of the endoplasmic reticulum and facilitates export by the formation of tunnel-like connections between the ER and Golgi. Hitherto, cargo-recognition appeared to be mediated by an SH3-like domain. Based on structural and dynamic data as well as interaction studies from NMR spectroscopy and microscale thermophoresis presented here, we show that the luminal cargo-recognition domain of TANGO1 adopts a new functional fold for which we suggest the term MOTH (MIA, Otoraplin, TALI/TANGO1 homology) domain. These MOTH domains, as well as an evolutionary intermediate found in invertebrates, constitute a distinct domain family that emerged from SH3 domains and acquired the ability to bind collagen.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomolecular Spectroscopy and RUBiospek|NMR, Faculty of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ruhr University of Bochum, Bochum, Germany.