Differential assembly diversifies GABA A receptor structures and signalling.
Sente, A., Desai, R., Naydenova, K., Malinauskas, T., Jounaidi, Y., Miehling, J., Zhou, X., Masiulis, S., Hardwick, S.W., Chirgadze, D.Y., Miller, K.W., Aricescu, A.R.(2022) Nature 604: 190-194
- PubMed: 35355020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04517-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QN5, 7QN6, 7QN7, 7QN8, 7QN9, 7QNA, 7QNB, 7QNC, 7QND, 7QNE - PubMed Abstract:
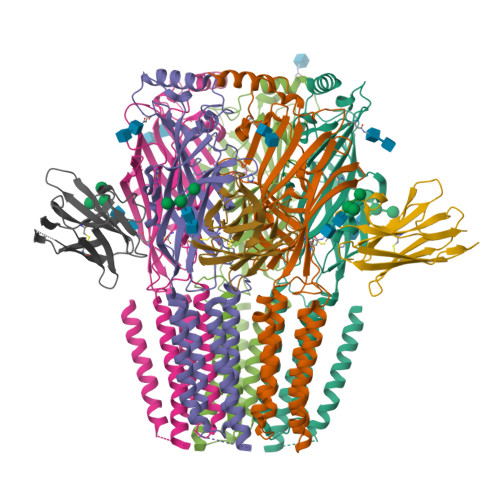
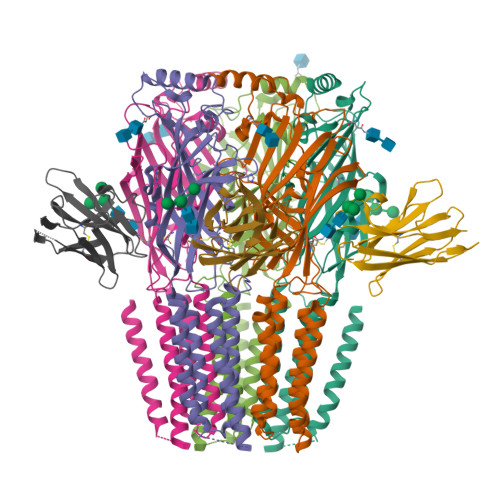
Type A γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABA A Rs) are pentameric ligand-gated chloride channels that mediate fast inhibitory signalling in neural circuits 1,2 and can be modulated by essential medicines including general anaesthetics and benzodiazepines 3 . Human GABA A R subunits are encoded by 19 paralogous genes that can, in theory, give rise to 495,235 receptor types. However, the principles that govern the formation of pentamers, the permutational landscape of receptors that may emerge from a subunit set and the effect that this has on GABAergic signalling remain largely unknown. Here we use cryogenic electron microscopy to determine the structures of extrasynaptic GABA A Rs assembled from α4, β3 and δ subunits, and their counterparts incorporating γ2 instead of δ subunits. In each case, we identified two receptor subtypes with distinct stoichiometries and arrangements, all four differing from those previously observed for synaptic, α1-containing receptors 4-7 . This, in turn, affects receptor responses to physiological and synthetic modulators by creating or eliminating ligand-binding sites at subunit interfaces. We provide structural and functional evidence that selected GABA A R arrangements can act as coincidence detectors, simultaneously responding to two neurotransmitters: GABA and histamine. Using assembly simulations and single-cell RNA sequencing data 8,9 , we calculated the upper bounds for receptor diversity in recombinant systems and in vivo. We propose that differential assembly is a pervasive mechanism for regulating the physiology and pharmacology of GABA A Rs.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK. asente@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk.