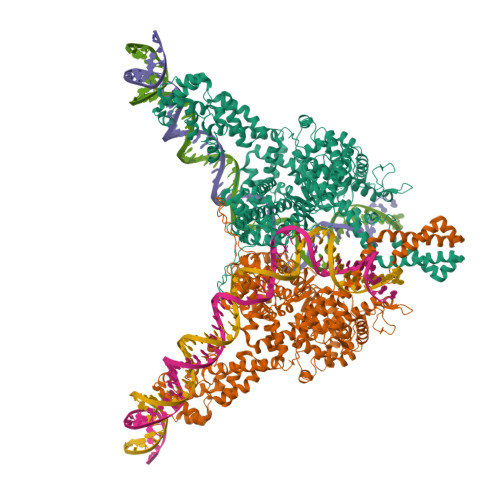
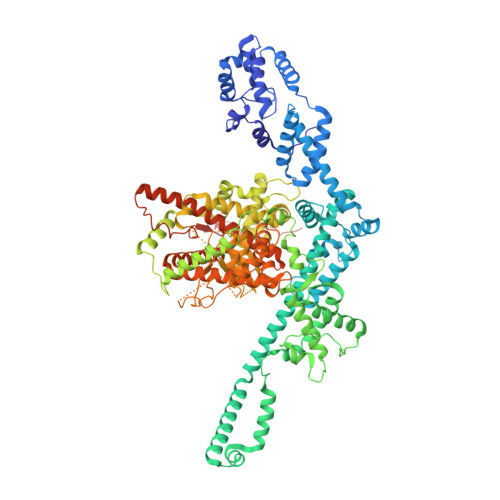
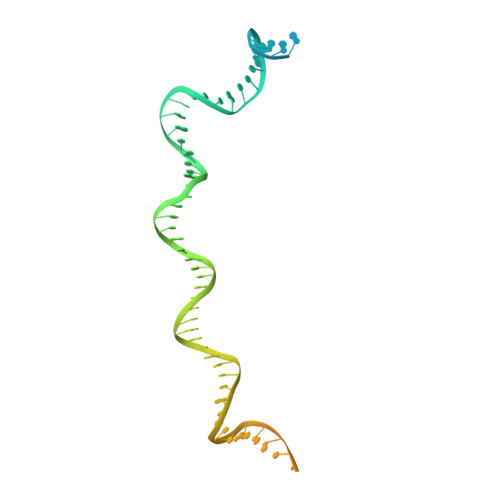
Structural insight into Tn3 family transposition mechanism.
Shkumatov, A.V., Aryanpour, N., Oger, C.A., Goossens, G., Hallet, B.F., Efremov, R.G.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 6155-6155
- PubMed: 36257990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33871-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QD4, 7QD5, 7QD6, 7QD8 - PubMed Abstract:
Transposons are diverse mobile genetic elements that play the critical role as genome architects in all domains of life. Tn3 is a widespread family and among the first identified bacterial transposons famed for their contribution to the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. Transposition within this family is mediated by a large TnpA transposase, which facilitates both transposition and target immunity. Howtever, a structural framework required for understanding the mechanism of TnpA transposition is lacking. Here, we describe the cryo-EM structures of TnpA from Tn4430 in the apo form and paired with transposon ends before and after DNA cleavage and strand transfer. We show that TnpA has an unusual architecture and exhibits a family specific regulatory mechanism involving metamorphic refolding of the RNase H-like catalytic domain. The TnpA structure, constrained by a double dimerization interface, creates a peculiar topology that suggests a specific role for the target DNA in transpososome assembly and activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Structural Biology, Vlaams Instituut voor Biotechnologie, Brussels, Belgium.