A scalable strategy to solve structures of PDZ domains and their complexes.
Cousido-Siah, A., Carneiro, L., Kostmann, C., Ecsedi, P., Nyitray, L., Trave, G., Gogl, G.(2022) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 78: 509-516
- PubMed: 35362473
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798322001784
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
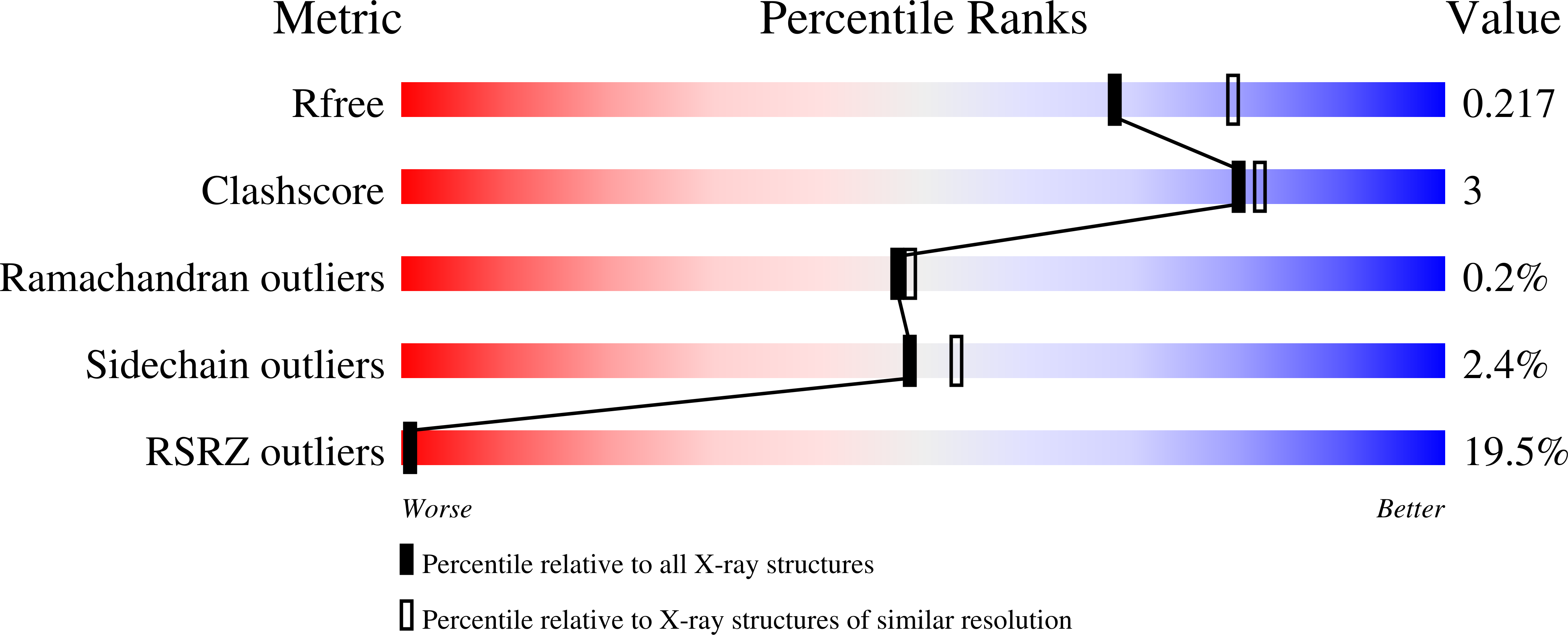
7PC3, 7PC4, 7PC5, 7PC7, 7PC8, 7PC9, 7PCB, 7QQL, 7QQM, 7QQN - PubMed Abstract:
The human PDZome represents one of the largest globular domain families in the human proteome, with 266 instances. These globular domains typically interact with C-terminal peptide motifs found in thousands of human proteins. Despite previous efforts, not all PDZ domains have experimentally solved structures and most of their complexes remain to be solved. Here, a simple and cost-effective strategy is proposed for the crystallization of PDZ domains and their complexes. A human annexin A2 fusion tag was used as a crystallization chaperone and the structures of nine PDZ domains were solved, including five domains that had not yet been solved. Finally, these novel experimental structures were compared with AlphaFold predictions and it is speculated how predictions and experimental methods could cooperate in order to investigate the structural landscapes of entire domain families and interactomes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Équipe Labellisée Ligue 2015, Département de Biologie Structurale Intégrative, Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire (IGBMC), INSERM U1258/CNRS UMR 7104/Université de Strasbourg, 1 Rue Laurent Fries, BP 10142, 67404 Illkirch, France.