Multiple Signals in the Gut Contract the Mouse Norovirus Capsid To Block Antibody Binding While Enhancing Receptor Affinity.
Williams, A.N., Sherman, M.B., Smith, H.Q., Taube, S., Pettitt, B.M., Wobus, C.E., Smith, T.J.(2021) J Virol 95: e0147121-e0147121
- PubMed: 34468172
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01471-21
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7N6Y, 7N7F - PubMed Abstract:
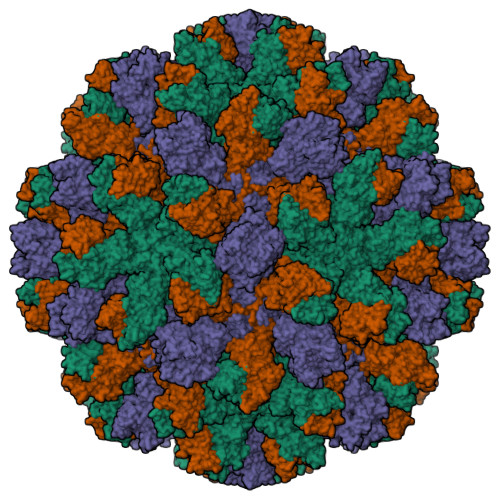
Human norovirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis worldwide, with no approved vaccine or antiviral treatment to mitigate infection. These plus-strand RNA viruses have T = 3 icosahedral protein capsids with 90 pronounced protruding (P) domain dimers, to which antibodies and cellular receptors bind. We previously demonstrated that bile binding to the capsid of mouse norovirus (MNV) causes several major conformational changes; the entire P domain rotates by ∼90° and contracts onto the shell, the P domain dimers rotate about each other, and the structural equilibrium of the epitopes at the top of the P domain shifts toward the closed conformation, which favors receptor binding while blocking antibody binding. Here, we demonstrate that MNV undergoes reversible conformational changes at pH 5.0 that are nearly identical to those observed when bile binds. Notably, at low pH or when metals bind, a cluster of acidic resides in the G'-H' loop interact and distort the G'-H' loop, and this may drive C'-D' loop movement toward the closed conformation. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with infectious virus particles at low pH or in the presence of metals demonstrated that all tested antibodies do not bind to this contracted form, akin to what was observed with the MNV-bile complex. Therefore, low pH, cationic metals, and bile salts are physiological triggers in the gut for P domain contraction and structural rearrangement, which synergistically prime the virus for receptor binding while blocking antibody binding. IMPORTANCE The protruding domains on the calicivirus capsids are recognized by cell receptors and antibodies. We demonstrated that MNV P domains are highly mobile, and bile causes contraction onto the shell surface while allosterically blocking antibody binding. We present the near-atomic cryo-electron microscopy structures of infectious MNV at pH 5.0 and pH 7.5. Surprisingly, low pH is sufficient to cause the same conformational changes as when bile binds. A cluster of acidic residues on the G'-H' loop were most likely involved in the pH effects. These residues also bound divalent cations and had the same conformation as observed here at pH 5. Binding assays demonstrated that low pH and metals block antibody binding, and thus the G'-H' loop might be driving the conformational changes. Therefore, low pH, cationic metals, and bile salts in the gut synergistically prime the virus for receptor binding while blocking antibody binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Galveston, Texas, USA.