Bacterial structural genomics target enabled by a recently discovered potent fungal acetyl-CoA synthetase inhibitor.
DeBouver, N.D., Bolejack, M.J., Esan, T.E., Krysan, D.J., Hagen, T.J., Abendroth, J.(2023) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun
- PubMed: 37223974
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X23003801
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
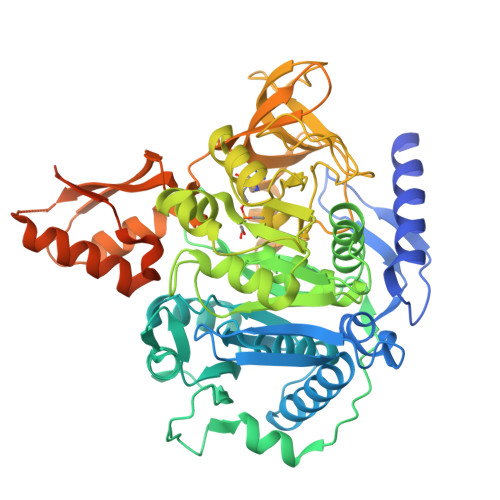
7MMZ - PubMed Abstract:
The compound ethyl-adenosyl monophosphate ester (ethyl-AMP) has been shown to effectively inhibit acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACS) enzymes and to facilitate the crystallization of fungal ACS enzymes in various contexts. In this study, the addition of ethyl-AMP to a bacterial ACS from Legionella pneumophila resulted in the determination of a co-crystal structure of this previously elusive structural genomics target. The dual functionality of ethyl-AMP in both inhibiting ACS enzymes and promoting crystallization establishes its significance as a valuable resource for advancing structural investigations of this class of proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
UCB Pharma, 7869 NE Day Road West, Bainbridge Island, WA 98102, USA.