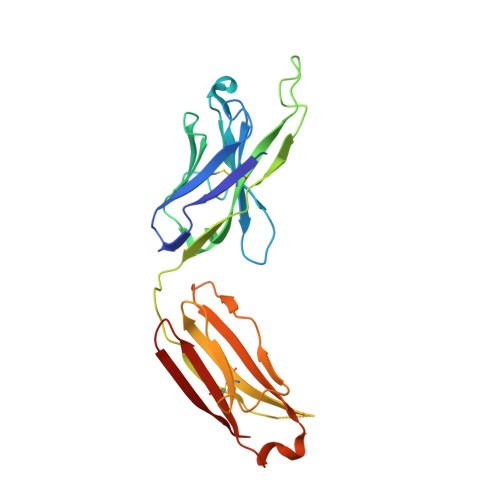
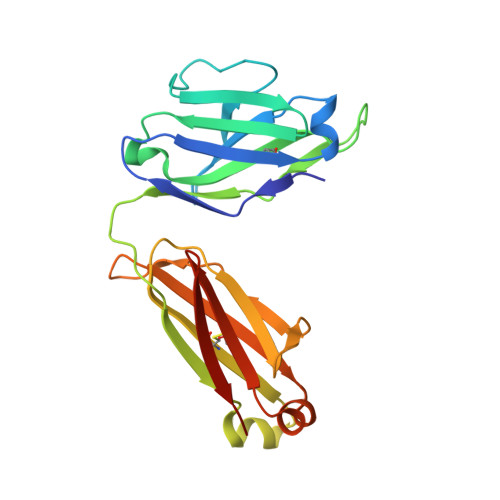
Structures of HIV-1 Neutralizing Antibody 10E8 Delineate the Mechanistic Basis of Its Multi-Peak Behavior on Size-Exclusion Chromatography.
Do Kwon, Y., Wang, X.E., Bender, M.F., Yang, R., Li, Y., McKee, K., Rawi, R., O'Dell, S., Schneck, N.A., Shaddeau, A., Zhang, B., Arnold, F.J., Connors, M., Doria-Rose, N.A., Kwong, P.D., Lei, Q.P.(2021) Antibodies (Basel) 10
- PubMed: 34200826
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antib10020023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7MF7, 7MF8, 7MF9, 7MFA, 7MFB - PubMed Abstract:
Antibody 10E8 is capable of effectively neutralizing HIV through its recognition of the membrane-proximal external region (MPER), and a suitably optimized version of 10E8 might have utility in HIV therapy and prophylaxis. However, 10E8 displays a three-peak profile on size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), complicating its manufacture. Here we show cis-trans conformational isomerization of the Tyr-Pro-Pro (YPP) motif in the heavy chain 3rd complementarity-determining region (CDR H3) of antibody 10E8 to be the mechanistic basis of its multipeak behavior. We observed 10E8 to undergo slow conformational isomerization and delineate a mechanistic explanation for effective comodifiers that were able to resolve its SEC heterogeneity and to allow an evaluation of the critical quality attribute of aggregation. We determined crystal structures of single and double alanine mutants of a key di-proline motif and of a light chain variant, revealing alternative conformations of the CDR H3. We also replicated both multi-peak and delayed SEC behavior with MPER-antibodies 4E10 and VRC42, by introducing a Tyr-Pro (YP) motif into their CDR H3s. Our results show how a conformationally dynamic CDR H3 can provide the requisite structural plasticity needed for a highly hydrophobic paratope to recognize its membrane-proximal epitope.
Organizational Affiliation:
Vaccine Research Center, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.