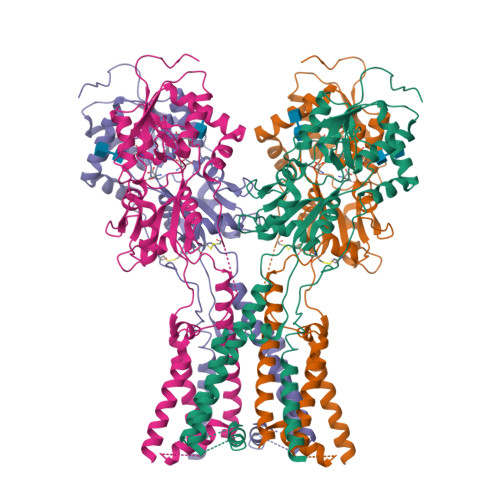
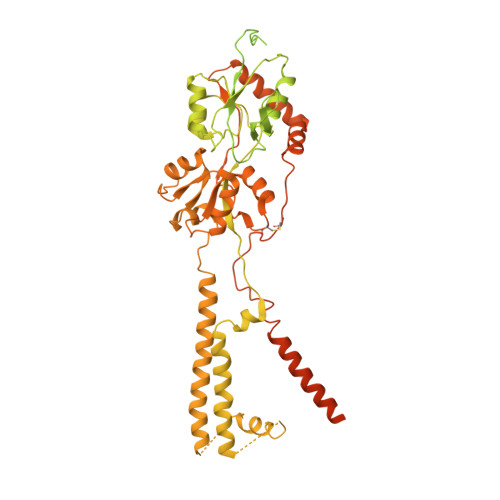
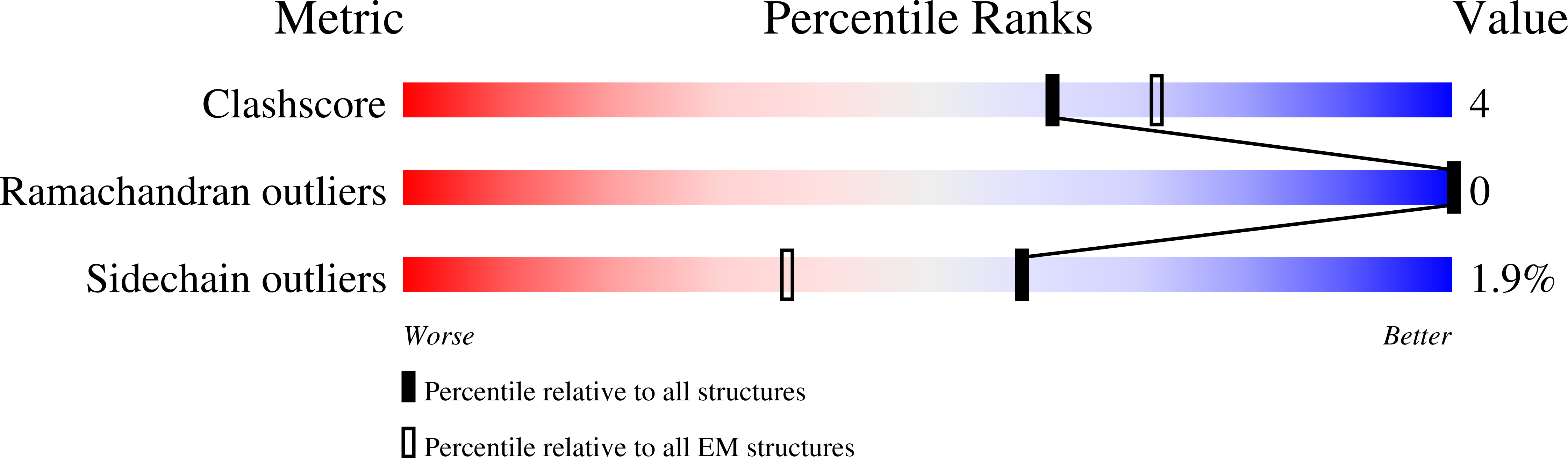Structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana glutamate receptor-like channel GLR3.4.
Green, M.N., Gangwar, S.P., Michard, E., Simon, A.A., Portes, M.T., Barbosa-Caro, J., Wudick, M.M., Lizzio, M.A., Klykov, O., Yelshanskaya, M.V., Feijo, J.A., Sobolevsky, A.I.(2021) Mol Cell 81: 3216
- PubMed: 34161757
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.05.025
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LZ0, 7LZ1, 7LZ2, 7LZH, 7LZI - PubMed Abstract:
Glutamate receptor-like channels (GLRs) play vital roles in various physiological processes in plants, such as wound response, stomatal aperture control, seed germination, root development, innate immune response, pollen tube growth, and morphogenesis. Despite the importance of GLRs, knowledge about their molecular organization is limited. Here we use X-ray crystallography and single-particle cryo-EM to solve structures of the Arabidopsis thaliana GLR3.4. Our structures reveal the tetrameric assembly of GLR3.4 subunits into a three-layer domain architecture, reminiscent of animal ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs). However, the non-swapped arrangement between layers of GLR3.4 domains, binding of glutathione through S-glutathionylation of cysteine C205 inside the amino-terminal domain clamshell, unique symmetry, inter-domain interfaces, and ligand specificity distinguish GLR3.4 from representatives of the iGluR family and suggest distinct features of the GLR gating mechanism. Our work elaborates on the principles of GLR architecture and symmetry and provides a molecular template for deciphering GLR-dependent signaling mechanisms in plants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, 650 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032, USA; Training Program in Nutritional and Metabolic Biology, Institute of Human Nutrition, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032, USA.