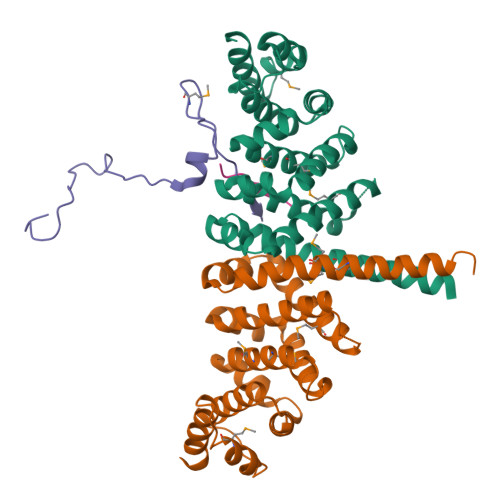
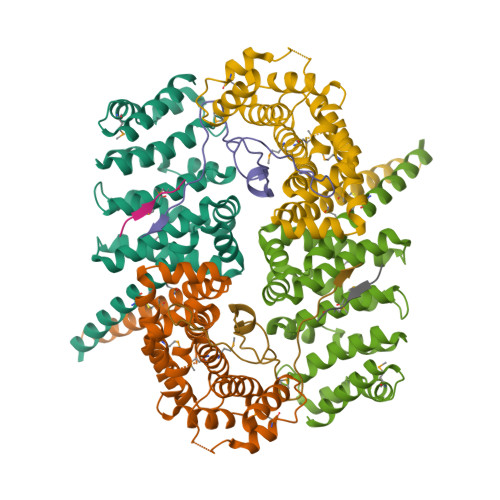
Structure of a meiosis-specific complex central to BRCA2 localization at recombination sites.
Pendlebury, D.F., Zhang, J., Agrawal, R., Shibuya, H., Nandakumar, J.(2021) Nat Struct Mol Biol 28: 671-680
- PubMed: 34373645
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00635-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LDG - PubMed Abstract:
Meiotic cells invoke breast cancer susceptibility gene 2 (BRCA2) to repair programmed double-stranded DNA breaks and accomplish homologous recombination. The meiosis-specific protein MEILB2 facilitates BRCA2 recruitment to meiotic recombination sites. Here, we combine crystallography, biochemical analysis and a mouse meiosis model to reveal a robust architecture that ensures meiotic BRCA2 recruitment. The crystal structure of the MEILB2-BRCA2 complex reveals how two MEILB2 homodimers sandwich two chains of BRCA2 to afford a 4:2 architecture. The sandwich lacks close contact between the two MEILB2 dimers or the two BRCA2 chains. Instead, the two halves of each BRCA2 chain bridge two MEILB2 subunits from different homodimers to form the MEILB2-BRCA2-MEILB2 sandwich. Several identical residues from the two MEILB2 subunits are employed to engage the BRCA2 halves, justifying their strict conservation. Mutational analysis of the interface reveals a synergistic mechanism for MEILB2-BRCA2 recruitment during meiosis. Overall, these studies demonstrate how BRCA2 efficiently localizes in the cell to facilitate meiosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA.