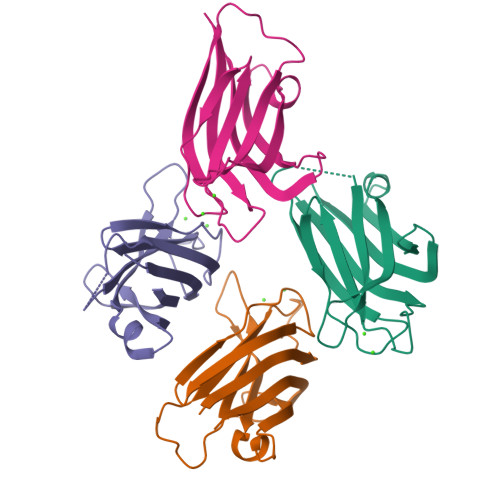
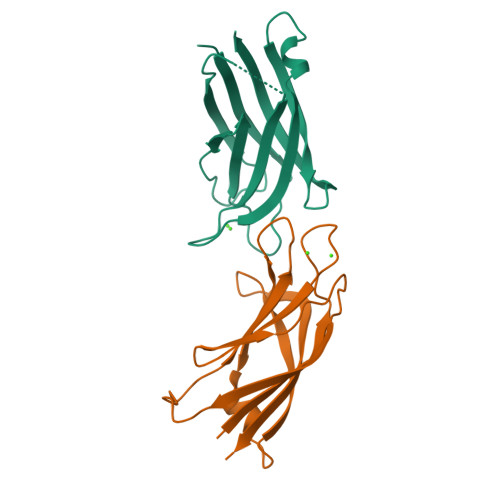
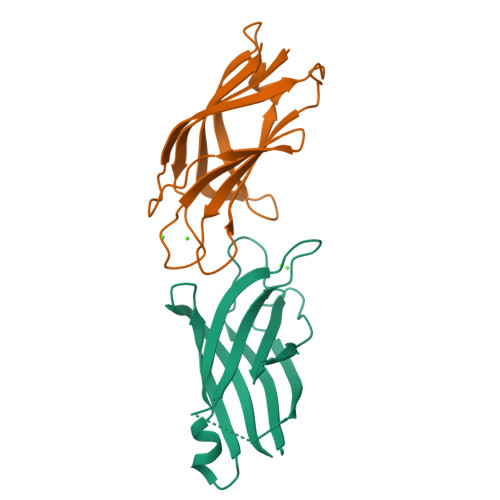
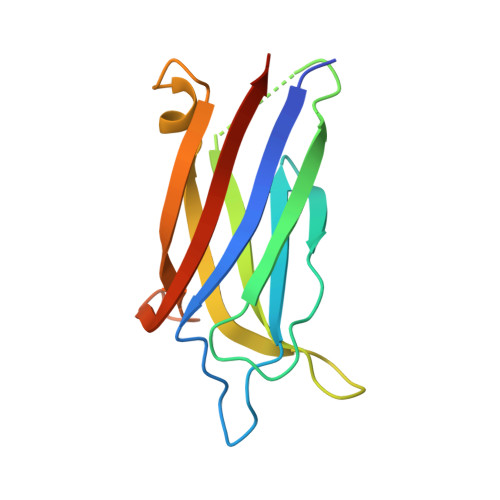
Calcium binds and rigidifies the dysferlin C2A domain in a tightly coupled manner.
Wang, Y., Tadayon, R., Santamaria, L., Mercier, P., Forristal, C.J., Shaw, G.S.(2021) Biochem J 478: 197-215
- PubMed: 33449082
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20200773
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JOF, 7K6B, 7KRB - PubMed Abstract:
The membrane protein dysferlin (DYSF) is important for calcium-activated plasma membrane repair, especially in muscle fibre cells. Nearly 600 mutations in the DYSF gene have been identified that are causative for rare genetic forms of muscular dystrophy. The dysferlin protein consists of seven C2 domains (C2A-C2G, 13%-33% identity) used to recruit calcium ions and traffic accessory proteins and vesicles to injured membrane sites needed to reseal a wound. Amongst these, the C2A is the most prominent facilitating the calcium-sensitive interaction with membrane surfaces. In this work, we determined the calcium-free and calcium-bound structures of the dysferlin C2A domain using NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. We show that binding two calcium ions to this domain reduces the flexibility of the Ca2+-binding loops in the structure. Furthermore, calcium titration and mutagenesis experiments reveal the tight coupling of these calcium-binding sites whereby the elimination of one site abolishes calcium binding to its partner site. We propose that the electrostatic potential distributed by the flexible, negatively charged calcium-binding loops in the dysferlin C2A domain control first contact with calcium that promotes subsequent binding. Based on these results, we hypothesize that dysferlin uses a 'calcium-catching' mechanism to respond to calcium influx during membrane repair.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, The University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5C1.