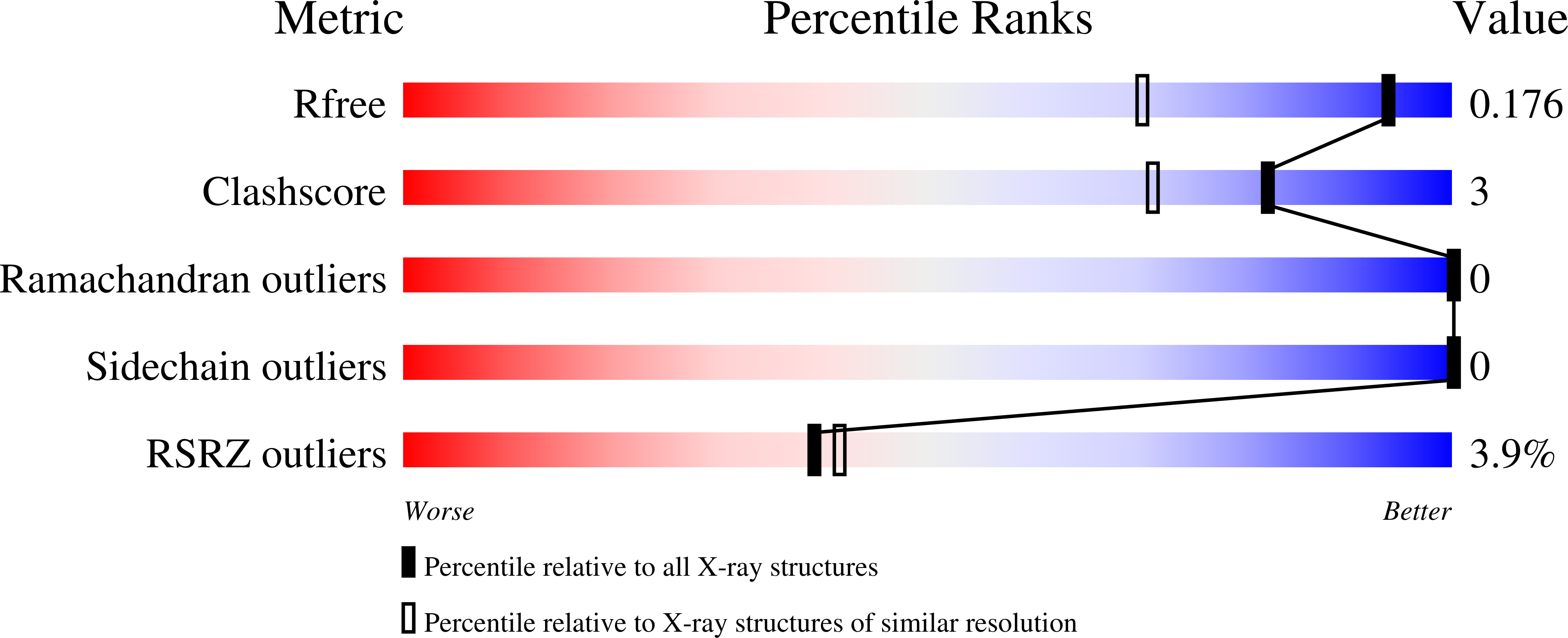
Structural Basis of Nanomolar Inhibition of Tumor-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase IX: X-Ray Crystallographic and Inhibition Study of Lipophilic Inhibitors with Acetazolamide Backbone.
Andring, J.T., Fouch, M., Akocak, S., Angeli, A., Supuran, C.T., Ilies, M.A., McKenna, R.(2020) J Med Chem 63: 13064-13075
- PubMed: 33085484
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01390
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JNR, 7JNV, 7JNW, 7JNX, 7JNZ, 7JO0, 7JO1, 7JO2, 7JO3, 7JOB, 7JOC - PubMed Abstract:
This study provides a structure-activity relationship study of a series of lipophilic carbonic anhydrase (CA) inhibitors with an acetazolamide backbone. The inhibitors were tested against the tumor-expressed CA isozyme IX (CA IX), and the cytosolic CA I, CA II, and membrane-bound CA IV. The study identified several low nanomolar potent inhibitors against CA IX, with lipophilicities spanning two log units. Very potent pan-inhibitors with nanomolar potency against CA IX and sub-nanomolar potency against CA II and CA IV, and with potency against CA I one order of magnitude better than the parent acetazolamide 1 were also identified in this study, together with compounds that displayed selectivity against membrane-bound CA IV. A comprehensive X-ray crystallographic study (12 crystal structures), involving both CA II and a soluble CA IX mimetic (CA IX-mimic), revealed the structural basis of this particular inhibition profile and laid the foundation for further developments toward more potent and selective inhibitors for the tumor-expressed CA IX.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32610, United States.