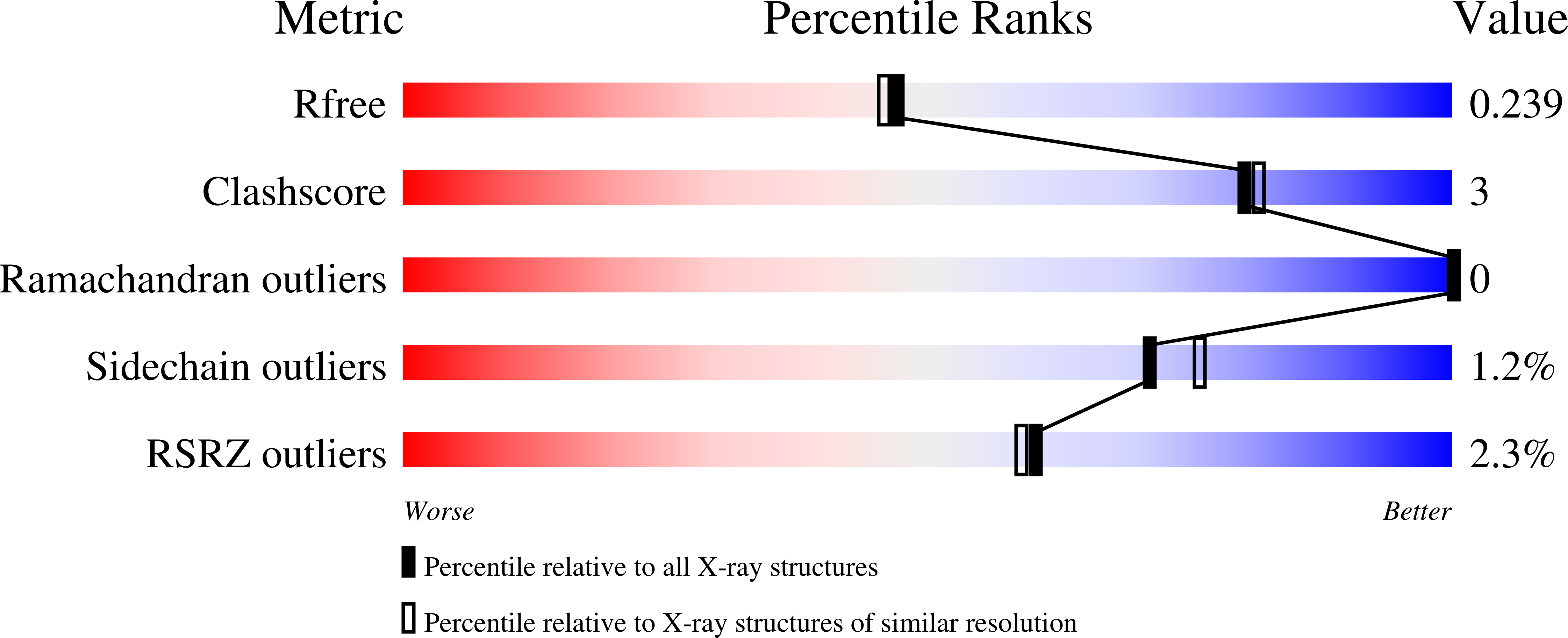
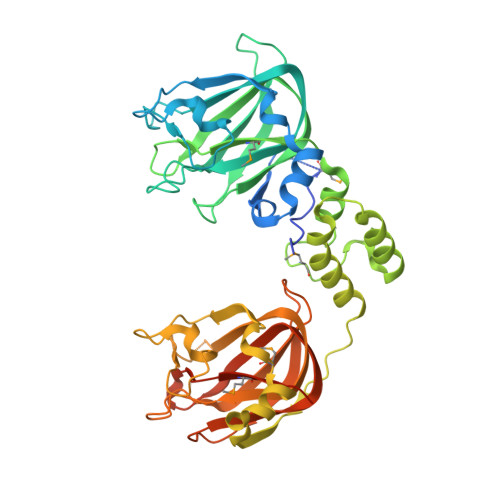
Architecturally complex O -glycopeptidases are customized for mucin recognition and hydrolysis.
Pluvinage, B., Ficko-Blean, E., Noach, I., Stuart, C., Thompson, N., McClure, H., Buenbrazo, N., Wakarchuk, W., Boraston, A.B.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33658366
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019220118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7JFS, 7JNB, 7JND, 7JNF, 7JRL, 7JRM, 7JS4 - PubMed Abstract:
A challenge faced by peptidases is the recognition of highly diverse substrates. A feature of some peptidase families is the capacity to specifically use post-translationally added glycans present on their protein substrates as a recognition determinant. This is ultimately critical to enabling peptide bond hydrolysis. This class of enzyme is also frequently large and architecturally sophisticated. However, the molecular details underpinning glycan recognition by these O -glycopeptidases, the importance of these interactions, and the functional roles of their ancillary domains remain unclear. Here, using the Clostridium perfringens ZmpA, ZmpB, and ZmpC M60 peptidases as model proteins, we provide structural and functional insight into how these intricate proteins recognize glycans as part of catalytic and noncatalytic substrate recognition. Structural, kinetic, and mutagenic analyses support the key role of glycan recognition within the M60 domain catalytic site, though they point to ZmpA as an apparently inactive enzyme. Wider examination of the Zmp domain content reveals noncatalytic carbohydrate binding as a feature of these proteins. The complete three-dimensional structure of ZmpB provides rare insight into the overall molecular organization of a highly multimodular enzyme and reveals how the interplay of individual domain function may influence biological activity. O -glycopeptidases frequently occur in host-adapted microbes that inhabit or attack mucus layers. Therefore, we anticipate that these results will be fundamental to informing more detailed models of how the glycoproteins that are abundant in mucus are destroyed as part of pathogenic processes or liberated as energy sources during normal commensal lifestyles.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC V8W 2Y2, Canada.