Synthesis of a Coumarin-Based PPAR gamma Fluorescence Probe for Competitive Binding Assay.
Yoshikawa, C., Ishida, H., Ohashi, N., Itoh, T.(2021) Int J Mol Sci 22
- PubMed: 33919837
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
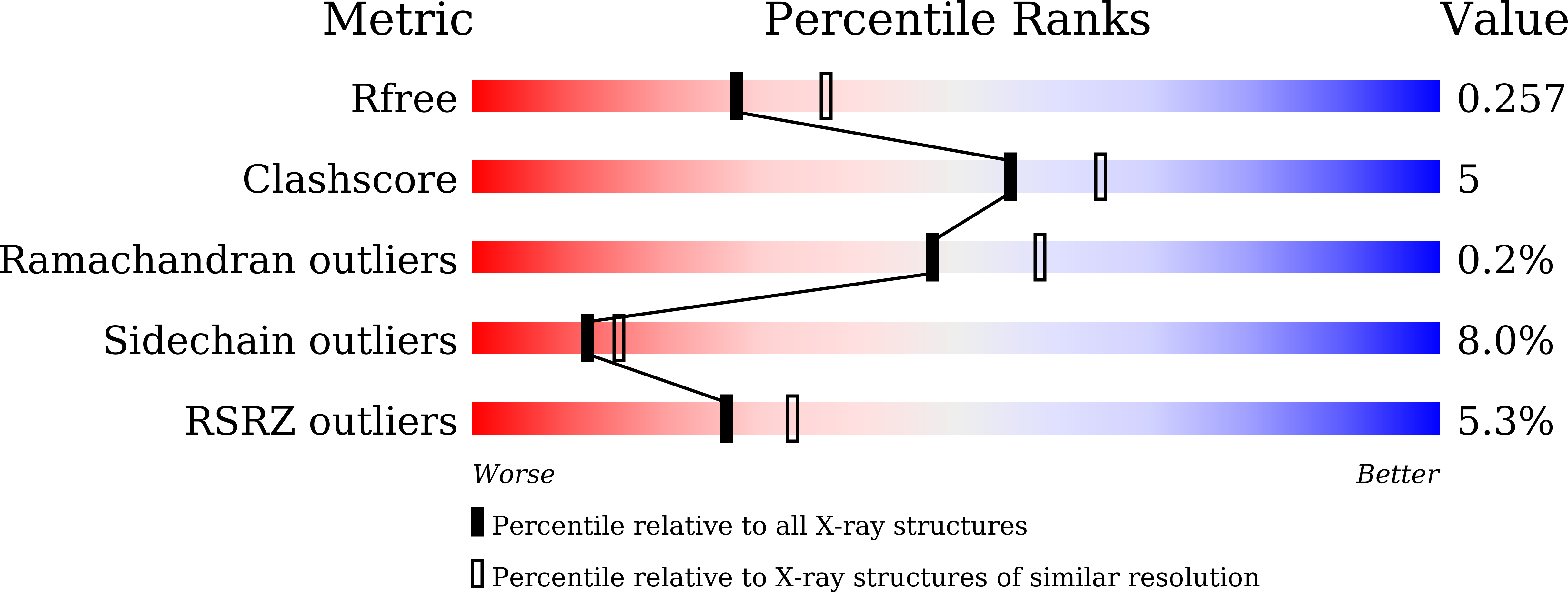
7EFQ - PubMed Abstract:
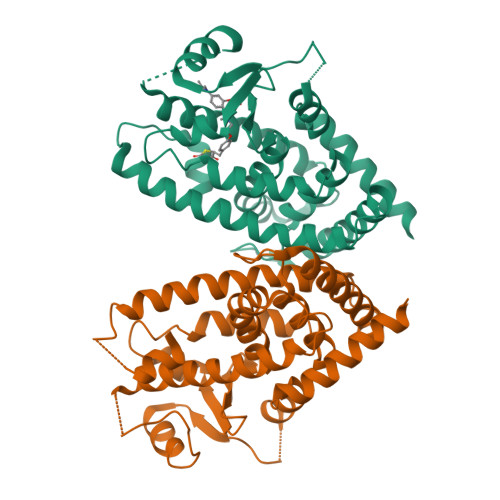
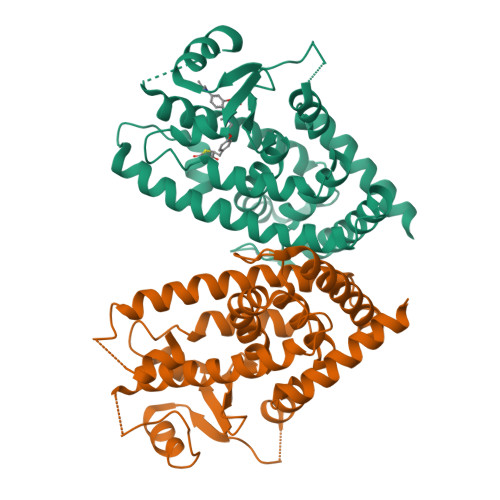
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a molecular target of metabolic syndrome and inflammatory disease. PPARγ is an important nuclear receptor and numerous PPARγ ligands were developed to date; thus, efficient assay methods are important. Here, we investigated the incorporation of 7-diethylamino coumarin into the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone and used the compound in a binding assay for PPARγ. PPARγ-ligand-incorporated 7-methoxycoumarin, 1 , showed weak fluorescence intensity in a previous report. We synthesized PPARγ-ligand-incorporating coumarin, 2 , in this report, and it enhanced the fluorescence intensity. The PPARγ ligand 2 maintained the rosiglitazone activity. The obtained partial agonist 6 appeared to act through a novel mechanism. The fluorescence intensity of 2 and 6 increased by binding to the ligand binding domain (LBD) of PPARγ and the affinity of reported PPARγ ligands were evaluated using the probe.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Drug Design and Medicinal Chemistry, Showa Pharmaceutical University, 3-3165 Higashi-Tamagawagakuen, Machida, Tokyo 194-8543, Japan.