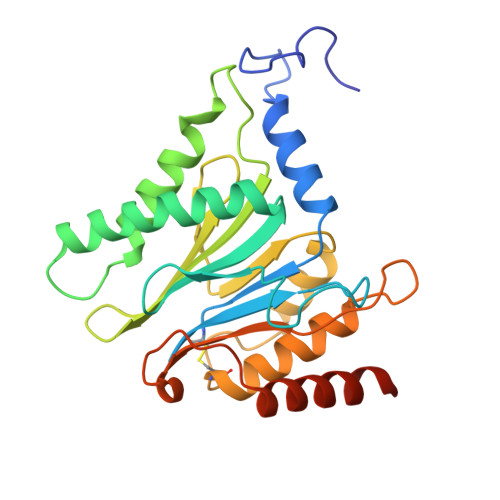
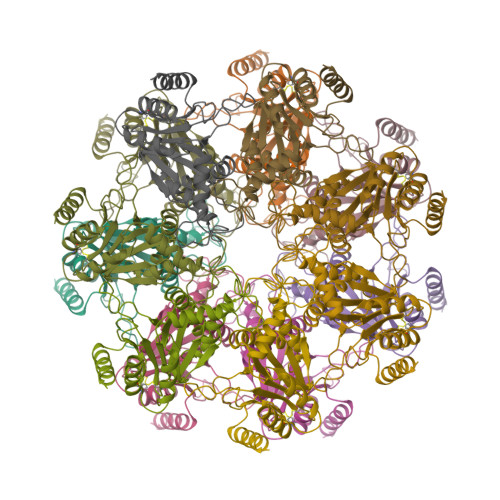
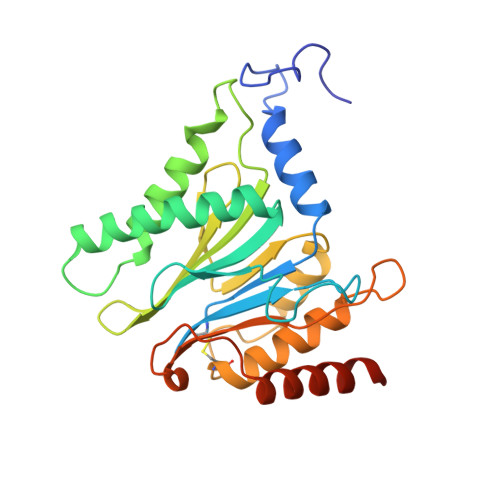
Structural Fluctuations of the Human Proteasome alpha 7 Homo-Tetradecamer Double Ring Imply the Proteasomal alpha-Ring Assembly Mechanism.
Song, C., Satoh, T., Sekiguchi, T., Kato, K., Murata, K.(2021) Int J Mol Sci 22
- PubMed: 33926037
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094519
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7E55 - PubMed Abstract:
The 20S proteasome, which is composed of layered α and β heptameric rings, is the core complex of the eukaryotic proteasome involved in proteolysis. The α7 subunit is a component of the α ring, and it self-assembles into a homo-tetradecamer consisting of two layers of α7 heptameric rings. However, the structure of the α7 double ring in solution has not been fully elucidated. We applied cryo-electron microscopy to delineate the structure of the α7 double ring in solution, revealing a structure different from the previously reported crystallographic model. The D7-symmetrical double ring was stacked with a 15° clockwise twist and a separation of 3 Å between the two rings. Two more conformations, dislocated and fully open, were also identified. Our observations suggest that the α7 double-ring structure fluctuates considerably in solution, allowing for the insertion of homologous α subunits, finally converting to the hetero-heptameric α rings in the 20S proteasome.
Organizational Affiliation:
Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems (ExCELLS), National Institutes of Natural Sciences, 5-1 Higashiyama, Myodaiji, Okazaki, Aichi 444-8787, Japan.