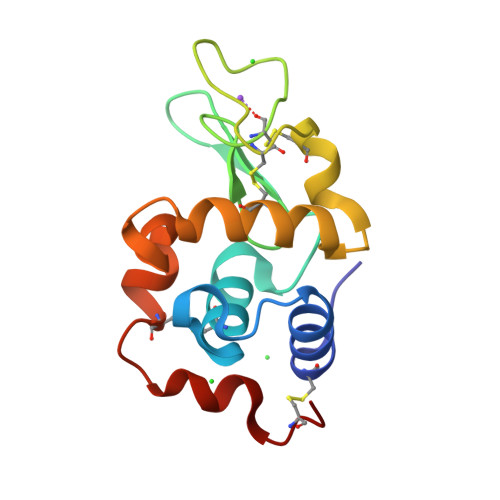
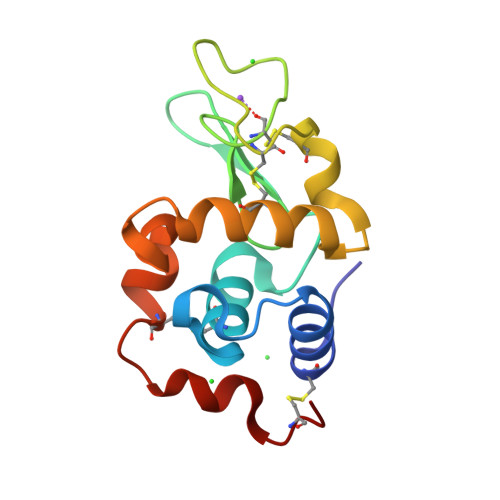
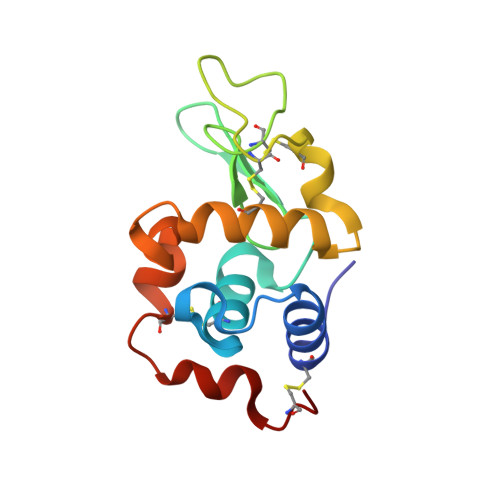
Recent structural insights into the mechanism of lysozyme hydrolysis.
Tanaka, I., Nishinomiya, R., Goto, R., Shimazaki, S., Chatake, T.(2021) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 77: 288-292
- PubMed: 33645532
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798321000346
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BR5, 7DEQ, 7DER - PubMed Abstract:
Lysozyme hydrolyzes the glycosidic bonds between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine in peptidoglycans located in the bacterial cell wall. The mechanism of the hydrolysis reaction of lysozyme was first studied more than 50 years ago; however, it has not yet been fully elucidated and various mechanisms are still being investigated. One reaction system that has commonly been proposed is that the lysozyme intermediate undergoes covalent ligand binding during hydrolysis. However, these findings resulted from experiments performed under laboratory conditions using fluorine-based ligands, which facilitate the formation of covalent bonds between the ligands and the catalytic side chain of lysozyme. More recently, high-resolution X-ray structural analysis was used to study the complex of lysozyme with an N-acetylglucosamine tetramer. As a result, the carboxyl group of Asp52 was found to form a relatively strong hydrogen-bond network and had difficulty binding covalently to C1 of the carbohydrate ring. To confirm this hydrogen-bond network, neutron test measurements were successfully performed to a resolution of better than 1.9 Å.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Ibaraki University, Hitachi, Ibaraki 316-8511, Japan.