Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase.
Ikuta, T., Shihoya, W., Sugiura, M., Yoshida, K., Watari, M., Tokano, T., Yamashita, K., Katayama, K., Tsunoda, S.P., Uchihashi, T., Kandori, H., Nureki, O.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 5605-5605
- PubMed: 33154353
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19376-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CJ3, 7D7P, 7D7Q - PubMed Abstract:
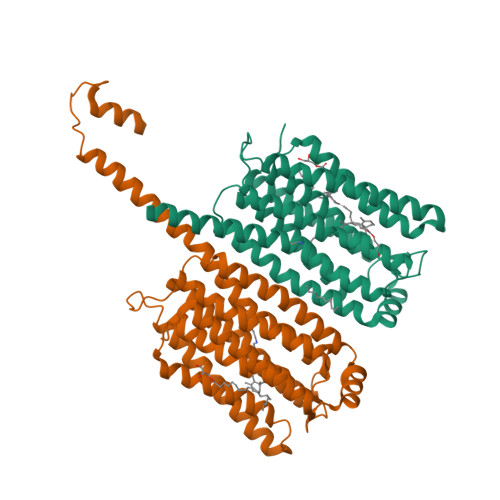
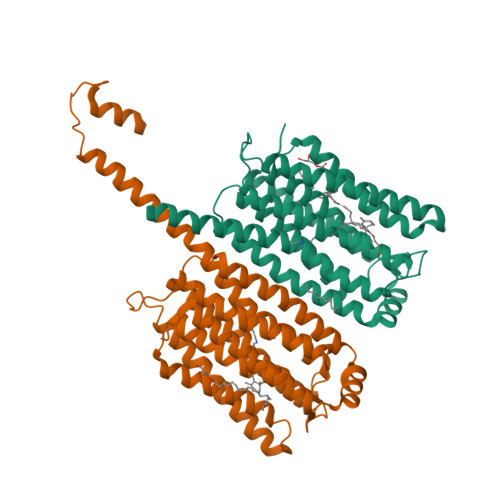
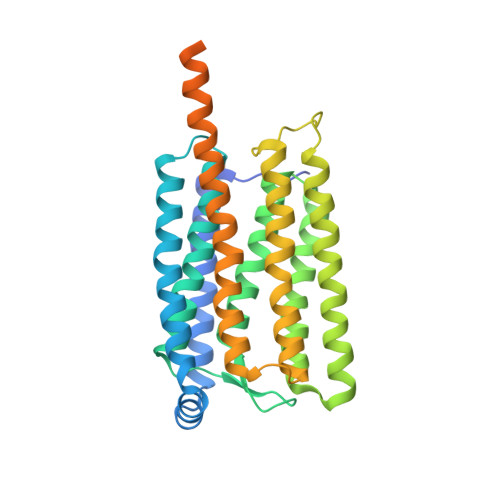
Rhodopsin phosphodiesterase (Rh-PDE) is an enzyme rhodopsin belonging to a recently discovered class of microbial rhodopsins with light-dependent enzymatic activity. Rh-PDE consists of the N-terminal rhodopsin domain and C-terminal phosphodiesterase (PDE) domain, connected by 76-residue linker, and hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP in a light-dependent manner. Thus, Rh-PDE has potential for the optogenetic manipulation of cyclic nucleotide concentrations, as a complementary tool to rhodopsin guanylyl cyclase and photosensitive adenylyl cyclase. Here we present structural and functional analyses of the Rh-PDE derived from Salpingoeca rosetta. The crystal structure of the rhodopsin domain at 2.6 Å resolution revealed a new topology of rhodopsins, with 8 TMs including the N-terminal extra TM, TM0. Mutational analyses demonstrated that TM0 plays a crucial role in the enzymatic photoactivity. We further solved the crystal structures of the rhodopsin domain (3.5 Å) and PDE domain (2.1 Å) with their connecting linkers, which showed a rough sketch of the full-length Rh-PDE. Integrating these structures, we proposed a model of full-length Rh-PDE, based on the HS-AFM observations and computational modeling of the linker region. These findings provide insight into the photoactivation mechanisms of other 8-TM enzyme rhodopsins and expand the definition of rhodopsins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan.