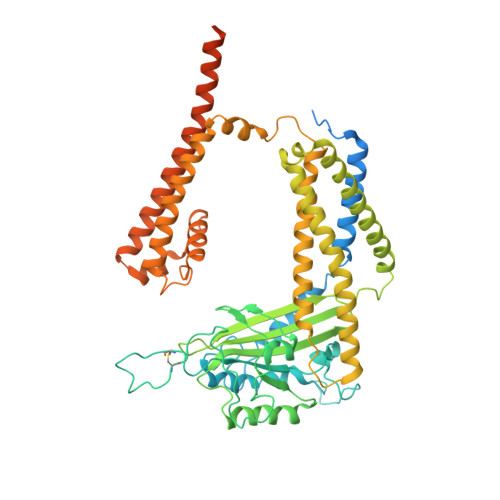
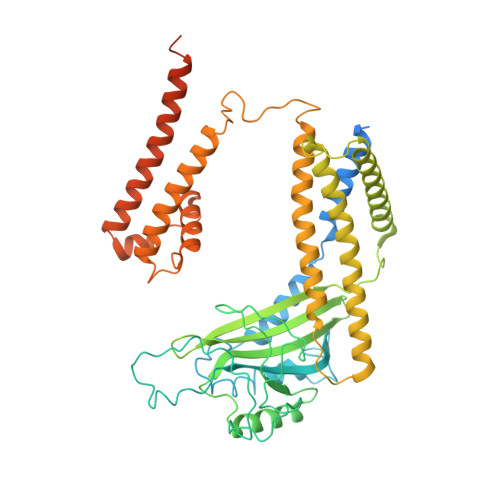
Structural basis for Ca 2+ activation of the heteromeric PKD1L3/PKD2L1 channel.
Su, Q., Chen, M., Wang, Y., Li, B., Jing, D., Zhan, X., Yu, Y., Shi, Y.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 4871-4871
- PubMed: 34381056
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25216-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7D7E, 7D7F - PubMed Abstract:
The heteromeric complex between PKD1L3, a member of the polycystic kidney disease (PKD) protein family, and PKD2L1, also known as TRPP2 or TRPP3, has been a prototype for mechanistic characterization of heterotetrametric TRP-like channels. Here we show that a truncated PKD1L3/PKD2L1 complex with the C-terminal TRP-fold fragment of PKD1L3 retains both Ca 2+ and acid-induced channel activities. Cryo-EM structures of this core heterocomplex with or without supplemented Ca 2+ were determined at resolutions of 3.1 Å and 3.4 Å, respectively. The heterotetramer, with a pseudo-symmetric TRP architecture of 1:3 stoichiometry, has an asymmetric selectivity filter (SF) guarded by Lys2069 from PKD1L3 and Asp523 from the three PKD2L1 subunits. Ca 2+ -entrance to the SF vestibule is accompanied by a swing motion of Lys2069 on PKD1L3. The S6 of PKD1L3 is pushed inward by the S4-S5 linker of the nearby PKD2L1 (PKD2L1-III), resulting in an elongated intracellular gate which seals the pore domain. Comparison of the apo and Ca 2+ -loaded complexes unveils an unprecedented Ca 2+ binding site in the extracellular cleft of the voltage-sensing domain (VSD) of PKD2L1-III, but not the other three VSDs. Structure-guided mutagenic studies support this unconventional site to be responsible for Ca 2+ -induced channel activation through an allosteric mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Structural Biology of Zhejiang Province, School of Life Sciences, Westlake University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. suqiang@westlake.edu.cn.