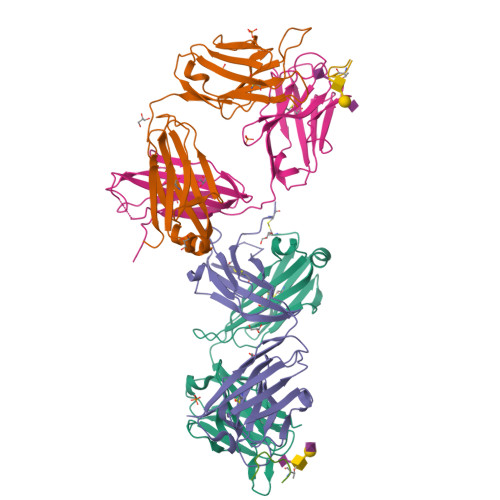
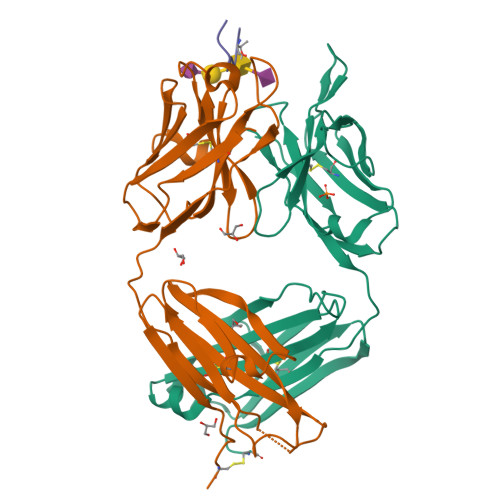
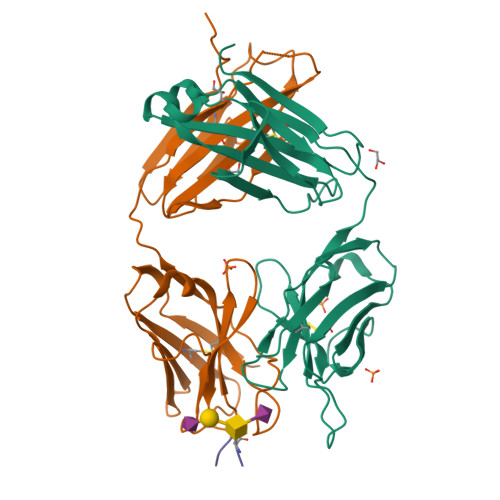
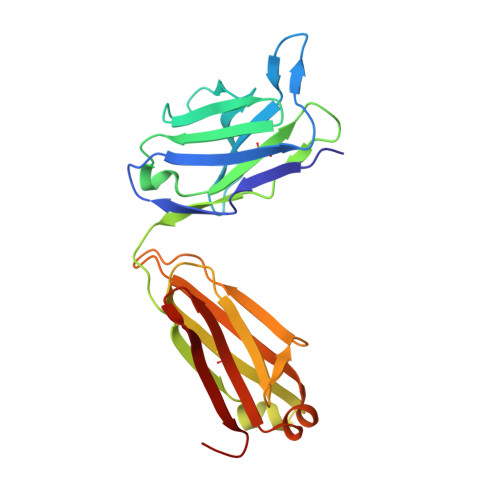
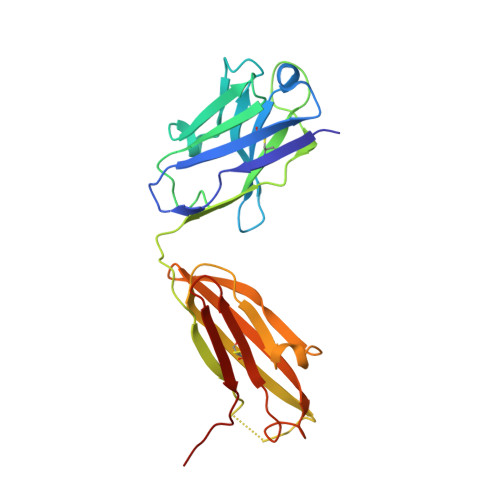
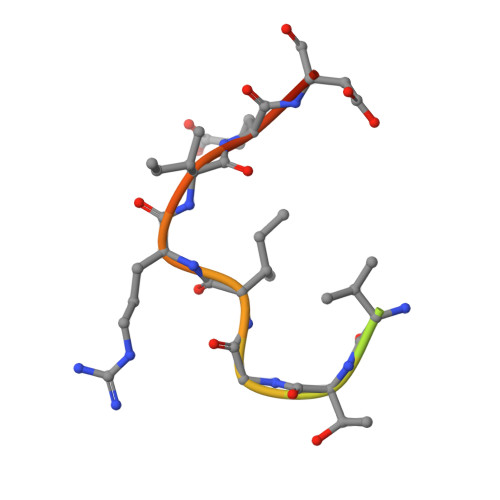
Crystal structure of an anti-podoplanin antibody bound to a disialylated O-linked glycopeptide.
Ogasawara, S., Suzuki, K., Naruchi, K., Nakamura, S., Shimabukuro, J., Tsukahara, N., Kaneko, M.K., Kato, Y., Murata, T.(2020) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 533: 57-63
- PubMed: 32921414
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.103
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7C94, 7C95 - PubMed Abstract:
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a highly O-glycosylated glycoprotein that is utilized as a specific lymphatic endothelial marker under pathophysiological conditions. We previously developed an anti-human PDPN (hPDPN) monoclonal antibody (mAb), clone LpMab-3, which recognizes the epitope, including both the peptides and the attached disialy-core-l (NeuAcα2-3Galβl-3 [NeuAcα2-6]GalNAcαl-O-Thr) structure at the Thr76 residue in hPDPN. However, it is unclear if the mAb binds directly to both the peptides and glycans. In this study, we synthesized the binding epitope region of LpMab-3 that includes the peptide (- 67 LVATSVNSV-T-GIRIEDLP 84 -) possessing a disialyl-core-1 O-glycan at Thr76, and we determined the crystal structure of the LpMab-3 Fab fragment that was bound to the synthesized glycopeptide at a 2.8 Å resolution. The six amino acid residues and two sialic acid residues are directly associated with four complementarity-determining regions (CDRs; H1, H2, H3, and L3) and four CDRs (H2, H3, L1, and L3), respectively. These results suggest that IgG is advantageous for generating binders against spacious epitopes such as glycoconjugates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Science, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan; Molecular Chirality Research Center, Chiba University, Chiba, Japan. Electronic address: satoshi-ogasawara@chiba-u.jp.