A novel sample delivery system based on circular motion for in situ serial synchrotron crystallography.
Zhao, F.Z., Sun, B., Yu, L., Xiao, Q.J., Wang, Z.J., Chen, L.L., Liang, H., Wang, Q.S., He, J.H., Yin, D.C.(2020) Lab Chip 20: 3888-3898
- PubMed: 32966481
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d0lc00443j
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7C09, 7C0P - PubMed Abstract:
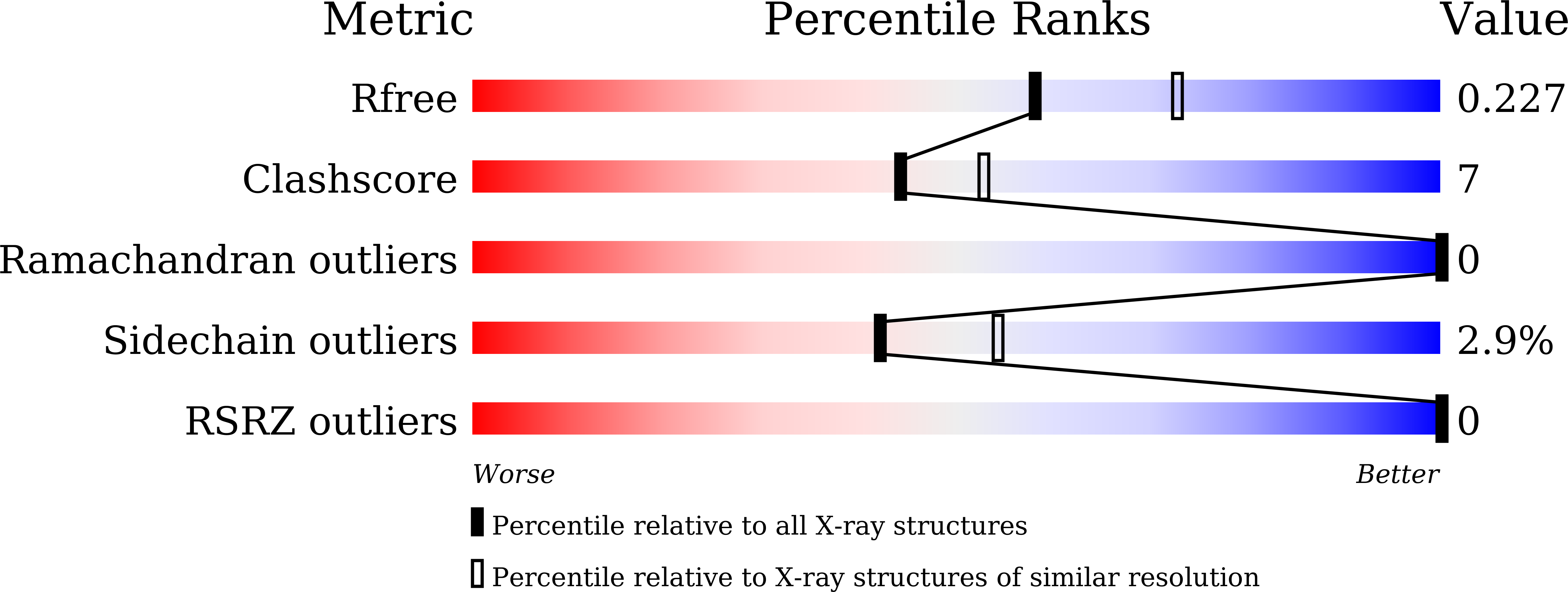
A sample delivery system is one of the key parts of serial crystallography. It is the main limiting factor affecting the application of serial crystallography. At present, although a variety of useful sample delivery systems have been developed for serial crystallography, it still remains the focus of the field to further improve the performance and efficiency of sample delivery. In existing sample delivery technologies, samples are usually delivered in linear motion. Here we show that the samples can also be delivered using circular motion, which is a novel motion mode never tested before. In this paper, we report a microfluidic rotating-target sample delivery device, which is characterized by the circular motion of the samples, and verify the performance of the device at a synchrotron radiation facility. The microfluidic rotating-target sample delivery device consists of two parts: a microfluidic sample plate and a motion control system. Sample delivery is realized by rotating the microfluidic sample plate containing in situ grown crystals. This device offers significant advantages, including a very wide adjustable range of delivery speed, low background noise, and low sample consumption. Using the microfluidic rotating-target device, we carried out in situ serial crystallography experiments with lysozyme and proteinase K as model samples at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, and performed structural determination based on the serial crystallographic data. The results showed that the designed device is fully compatible with the synchrotron radiation facility, and the structure determination of proteins is successful using the serial crystallographic data obtained with the device.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, China. yindc@nwpu.edu.cn.