Structural basis of intron selection by U2 snRNP in the presence of covalent inhibitors.
Cretu, C., Gee, P., Liu, X., Agrawal, A., Nguyen, T.V., Ghosh, A.K., Cook, A., Jurica, M., Larsen, N.A., Pena, V.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 4491-4491
- PubMed: 34301950
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24741-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7B0I, 7B91, 7B92, 7B9C, 7OMF, 7ONB, 7OPI - PubMed Abstract:
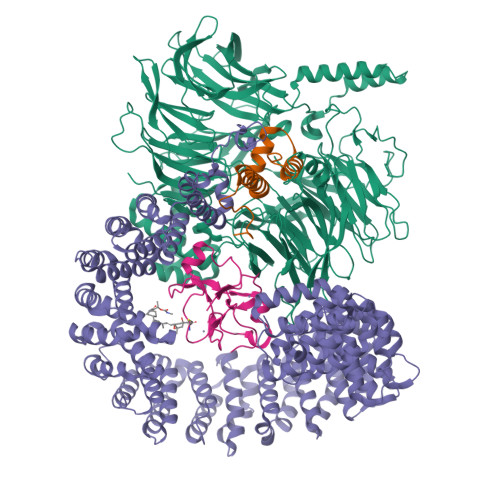
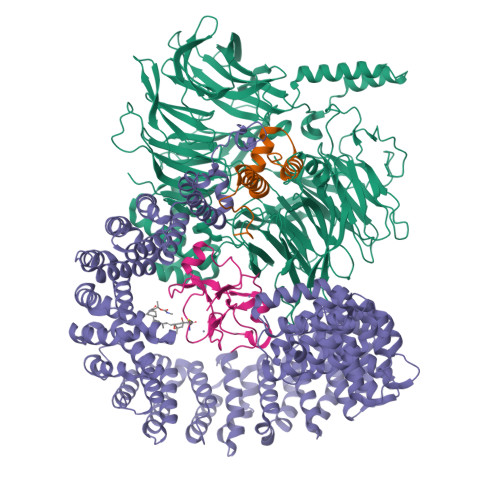
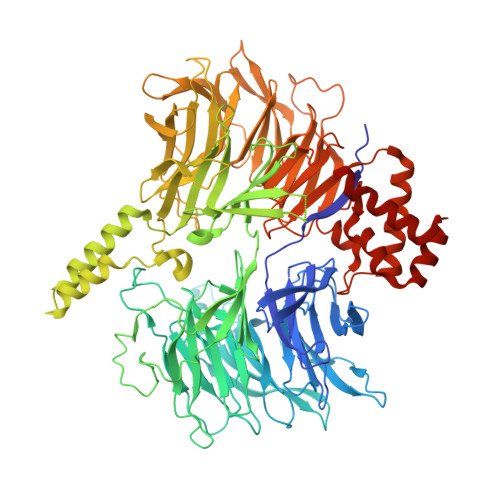
Intron selection during the formation of prespliceosomes is a critical event in pre-mRNA splicing. Chemical modulation of intron selection has emerged as a route for cancer therapy. Splicing modulators alter the splicing patterns in cells by binding to the U2 snRNP (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein)-a complex chaperoning the selection of branch and 3' splice sites. Here we report crystal structures of the SF3B module of the U2 snRNP in complex with spliceostatin and sudemycin FR901464 analogs, and the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a cross-exon prespliceosome-like complex arrested with spliceostatin A. The structures reveal how modulators inactivate the branch site in a sequence-dependent manner and stall an E-to-A prespliceosome intermediate by covalent coupling to a nucleophilic zinc finger belonging to the SF3B subunit PHF5A. These findings support a mechanism of intron recognition by the U2 snRNP as a toehold-mediated strand invasion and advance an unanticipated drug targeting concept.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Group Mechanisms and Regulation of Splicing, The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UK.