Imidazo[1,2-c]pyrimidin-5(6H)-one inhibitors of CDK2: Synthesis, kinase inhibition and co-crystal structure.
Jansa, J., Jorda, R., Skerlova, J., Pachl, P., Perina, M., Reznickova, E., Heger, T., Gucky, T., Rezacova, P., Lycka, A., Krystof, V.(2021) Eur J Med Chem 216: 113309-113309
- PubMed: 33711765
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113309
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ACK - PubMed Abstract:
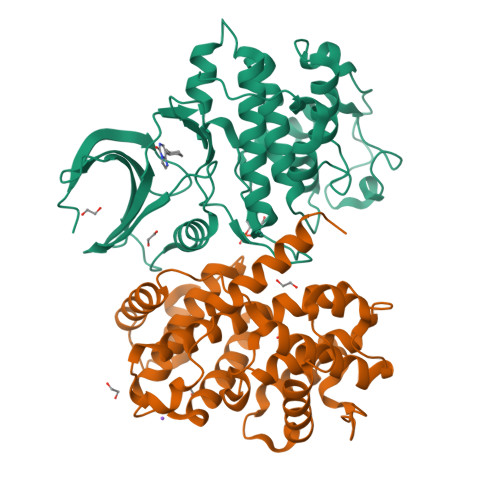
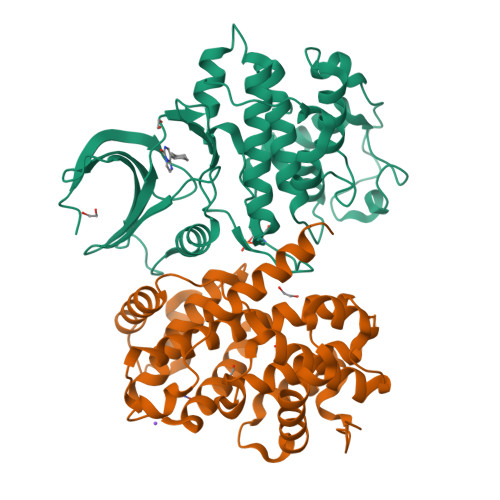
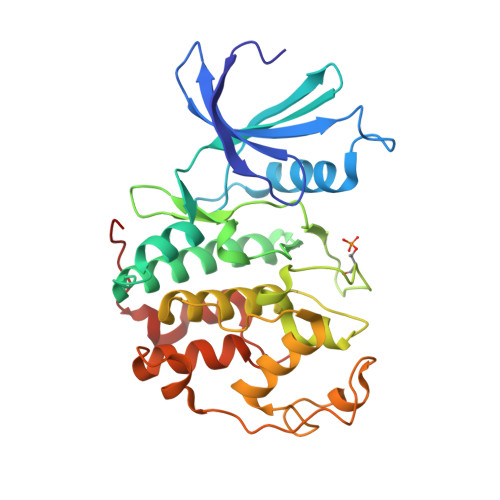
Pharmacological inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases has emerged as a possible treatment option for various cancer types. We recently identified substituted imidazo[1,2-c]pyrimidin-5(6H)-ones as inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2). Here, we report the synthesis of derivatives modified at positions 2, 3, 6 or 8 prepared using Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling, halogenation, Dimroth-type rearrangement and alkylation as the main synthetic methods. The compounds displayed micro- to submicromolar inhibition of CDK2/cyclin E activity. Binding of the most potent compound 3b to CDK2 was determined using isothermal titration calorimetry. The co-crystal structure of 3b in complex with fully active CDK2 was solved, revealing the binding mode of 3b in the ATP pocket and a hydrogen bonding interaction with hinge region residue Leu83. Evaluation against leukaemia cell lines revealed low cytotoxicity, which is in line with the high selectivity towards CDK2. This study demonstrates that substituted imidazo[1,2-c]pyrimidines can be exploited for future kinase inhibitor development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Institute for Organic Syntheses (VUOS), Rybitví 296, 53354, Pardubice-Rybitví, Czech Republic.