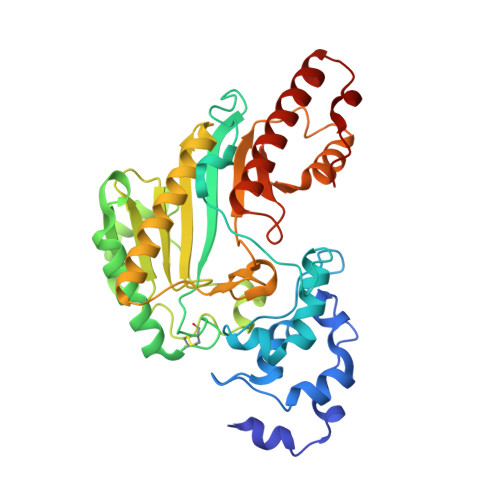
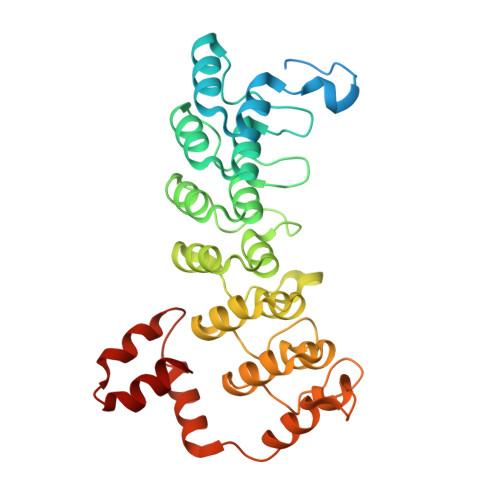
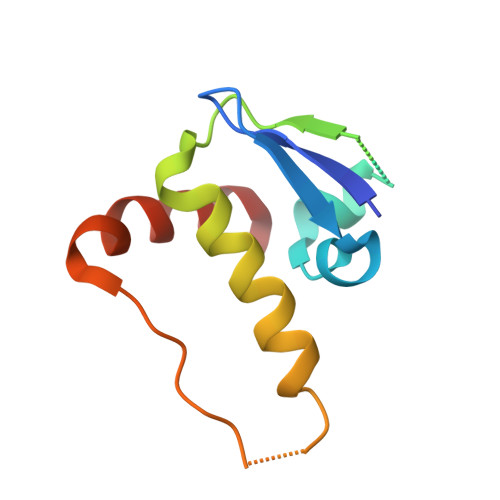
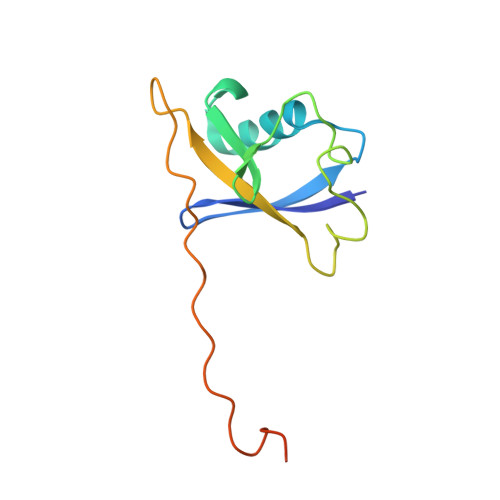
Structure and dynamics of the ASB9 CUL-RING E3 Ligase.
Lumpkin, R.J., Baker, R.W., Leschziner, A.E., Komives, E.A.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 2866-2866
- PubMed: 32513959
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16499-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V9H, 6V9I - PubMed Abstract:
The Cullin 5 (CUL5) Ring E3 ligase uses adaptors Elongins B and C (ELOB/C) to bind different SOCS-box-containing substrate receptors, determining the substrate specificity of the ligase. The 18-member ankyrin and SOCS box (ASB) family is the largest substrate receptor family. Here we report cryo-EM data for the substrate, creatine kinase (CKB) bound to ASB9-ELOB/C, and for full-length CUL5 bound to the RING protein, RBX2, which binds various E2s. To date, no full structures are available either for a substrate-bound ASB nor for CUL5. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange (HDX-MS) mapped onto a full structural model of the ligase revealed long-range allostery extending from the substrate through CUL5. We propose a revised allosteric mechanism for how CUL-E3 ligases function. ASB9 and CUL5 behave as rigid rods, connected through a hinge provided by ELOB/C transmitting long-range allosteric crosstalk from the substrate through CUL5 to the RBX2 flexible linker.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA, 92092-0378, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: