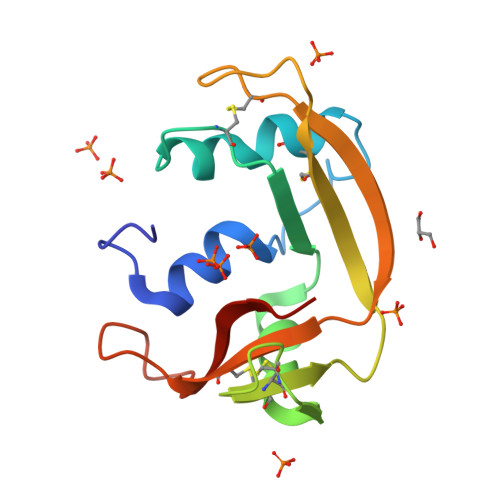
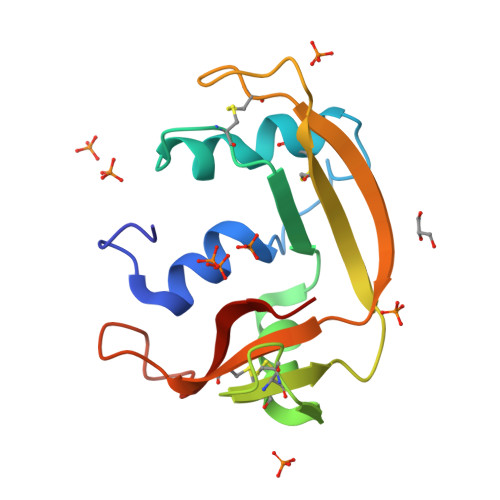
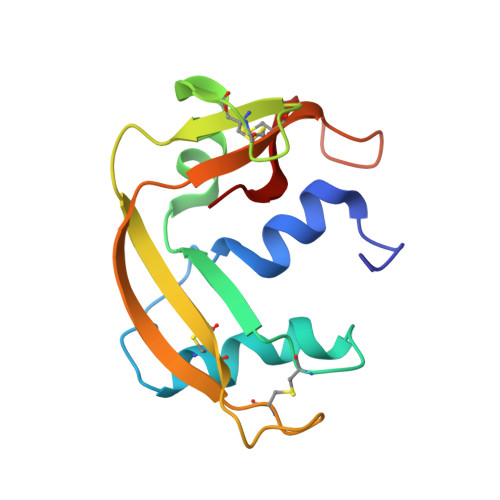
Exploring the RNase A scaffold to combine catalytic and antimicrobial activities. Structural characterization of RNase 3/1 chimeras.
Fernandez-Millan, P., Vazquez-Monteagudo, S., Boix, E., Prats-Ejarque, G.(2022) Front Mol Biosci 9: 964717-964717
- PubMed: 36188223
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.964717
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6SSN, 6YBC, 6YBE, 6YMT - PubMed Abstract:
Design of novel antibiotics to fight antimicrobial resistance is one of the first global health priorities. Novel protein-based strategies come out as alternative therapies. Based on the structure-function knowledge of the RNase A superfamily we have engineered a chimera that combines RNase 1 highest catalytic activity with RNase 3 unique antipathogen properties. A first construct (RNase 3/1-v1) was successfully designed with a catalytic activity 40-fold higher than RNase 3, but alas in detriment of its anti-pathogenic activity. Next, two new versions of the original chimeric protein were created showing improvement in the antimicrobial activity. Both second generation versions (RNases 3/1-v2 and -v3) incorporated a loop characteristic of RNase 3 (L7), associated to antimicrobial activity. Last, removal of an RNase 1 flexible loop (L1) in the third version enhanced its antimicrobial properties and catalytic efficiency. Here we solved the 3D structures of the three chimeras at atomic resolution by X-ray crystallography. Structural analysis outlined the key functional regions. Prediction by molecular docking of the protein chimera in complex with dinucleotides highlighted the contribution of the C-terminal region to shape the substrate binding cavity and determine the base selectivity and catalytic efficiency. Nonetheless, the structures that incorporated the key features related to RNase 3 antimicrobial activity retained the overall RNase 1 active site conformation together with the essential structural elements for binding to the human ribonuclease inhibitor (RNHI), ensuring non-cytotoxicity. Results will guide us in the design of the best RNase pharmacophore for anti-infective therapies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Biosciences, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Cerdanyola del Vallès, Spain.