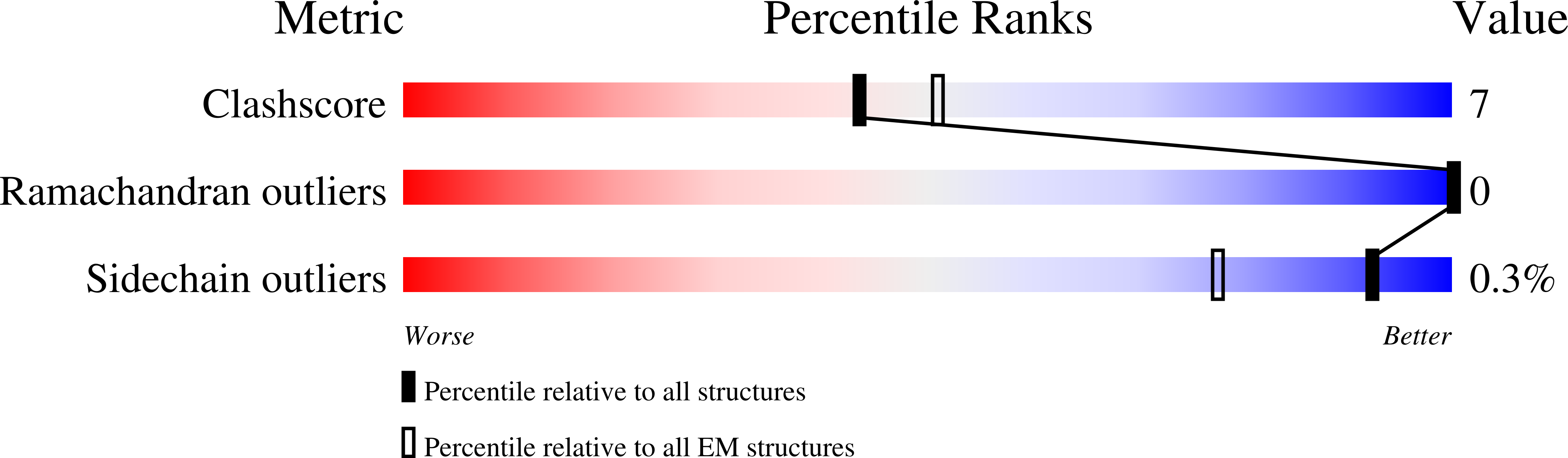Phospho-regulation, nucleotide binding and ion access control in potassium-chloride cotransporters.
Chi, G., Ebenhoch, R., Man, H., Tang, H., Tremblay, L.E., Reggiano, G., Qiu, X., Bohstedt, T., Liko, I., Almeida, F.G., Garneau, A.P., Wang, D., McKinley, G., Moreau, C.P., Bountra, K.D., Abrusci, P., Mukhopadhyay, S.M.M., Fernandez-Cid, A., Slimani, S., Lavoie, J.L., Burgess-Brown, N.A., Tehan, B., DiMaio, F., Jazayeri, A., Isenring, P., Robinson, C.V., Durr, K.L.(2021) EMBO J 40: e107294-e107294
- PubMed: 34031912
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020107294
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Y5V, 7AIN, 7AIO, 7AIP, 7AIQ, 7AIR, 7NGB - PubMed Abstract:
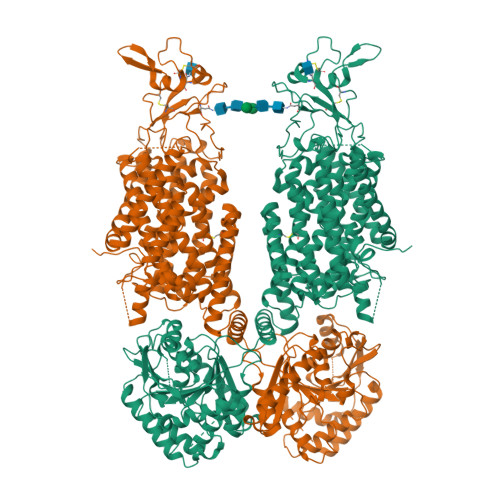
Potassium-coupled chloride transporters (KCCs) play crucial roles in regulating cell volume and intracellular chloride concentration. They are characteristically inhibited under isotonic conditions via phospho-regulatory sites located within the cytoplasmic termini. Decreased inhibitory phosphorylation in response to hypotonic cell swelling stimulates transport activity, and dysfunction of this regulatory process has been associated with various human diseases. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human KCC3b and KCC1, revealing structural determinants for phospho-regulation in both N- and C-termini. We show that phospho-mimetic KCC3b is arrested in an inward-facing state in which intracellular ion access is blocked by extensive contacts with the N-terminus. In another mutant with increased isotonic transport activity, KCC1Δ19, this interdomain interaction is absent, likely due to a unique phospho-regulatory site in the KCC1 N-terminus. Furthermore, we map additional phosphorylation sites as well as a previously unknown ATP/ADP-binding pocket in the large C-terminal domain and show enhanced thermal stabilization of other CCCs by adenine nucleotides. These findings provide fundamentally new insights into the complex regulation of KCCs and may unlock innovative strategies for drug development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Nuffield Department of Medicine, Centre of Medicines Discovery, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.