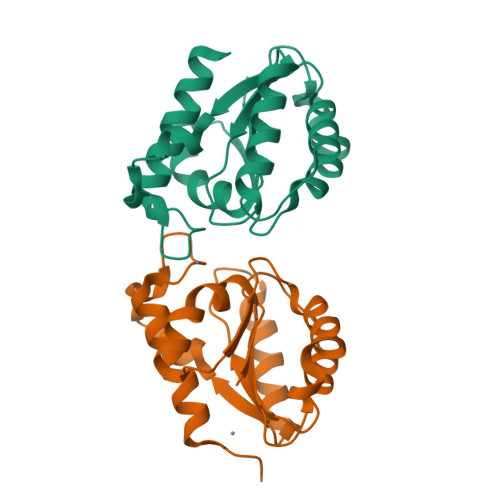
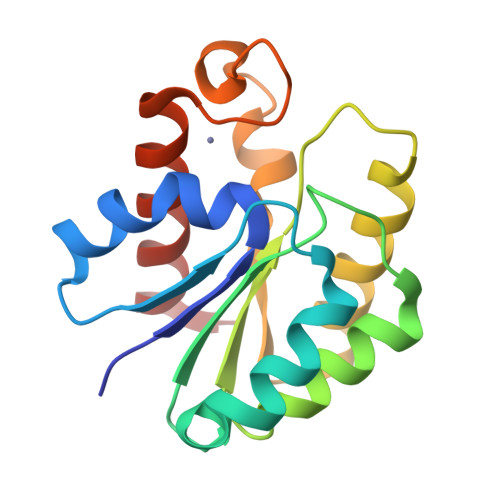
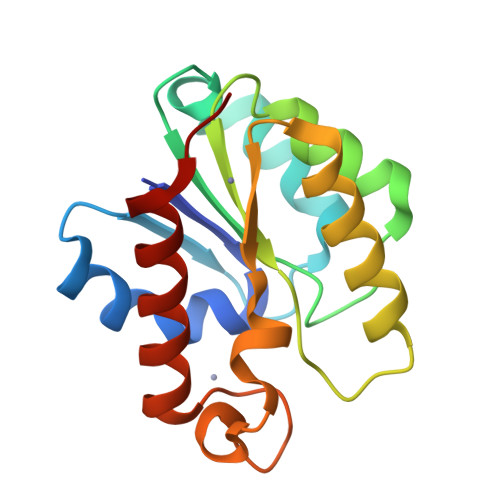
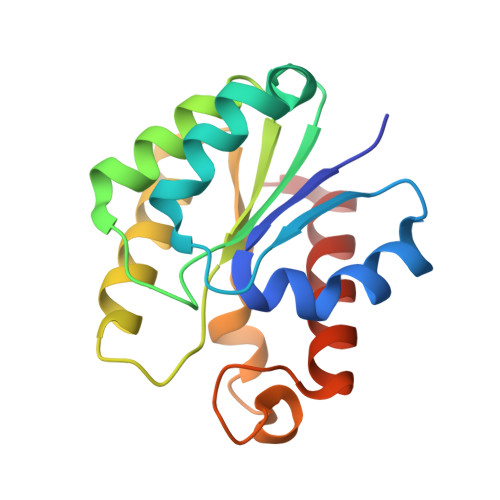
Structural basis for theO-acetyltransferase function of the extracytoplasmic domain of OatA fromStaphylococcus aureus.
Jones, C.S., Sychantha, D., Howell, P.L., Clarke, A.J.(2020) J Biological Chem 295: 8204-8213
- PubMed: 32350117
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.013108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VJP, 6WN9 - PubMed Abstract:
Many bacteria possess enzymes that modify the essential cell-wall polymer peptidoglycan by O -acetylation. This modification occurs in numerous Gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , a common cause of human infections. O -Acetylation of peptidoglycan protects bacteria from the lytic activity of lysozyme, a mammalian innate immune enzyme, and as such is important for bacterial virulence. The O -acetylating enzyme in Gram-positive bacteria, O -acetyltransferase A (OatA), is a two-domain protein consisting of an N-terminal integral membrane domain and a C-terminal extracytoplasmic domain. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structure at 1.71 Å resolution and the biochemical characterization of the C-terminal domain of S. aureus OatA. The structure revealed that this OatA domain adopts an SGNH-hydrolase fold and possesses a canonical catalytic triad. Site-specific replacement of active-site amino acids revealed the presence of a water-coordinating aspartate residue that limits esterase activity. This residue, although conserved in staphyloccocal OatA and most other homologs, is not present in the previously characterized streptococcal OatA. These results provide insights into the mechanism of acetyl transfer in the SGNH/GDSL hydrolase family and highlight important evolutionary differences between homologous OatA enzymes. Furthermore, this study enhances our understanding of PG O -acetyltransferases, which could guide the development of novel antibacterial drugs to combat infections with multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada.