Structural Insights into Ceftobiprole Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Penicillin-Binding Protein 3.
Kumar, V., Tang, C., Bethel, C.R., Papp-Wallace, K.M., Wyatt, J., Desarbre, E., Bonomo, R.A., van den Akker, F.(2020) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 64
- PubMed: 32152075
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00106-20
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VJE - PubMed Abstract:
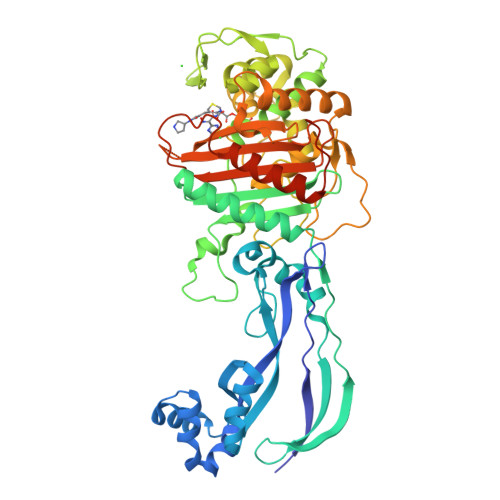
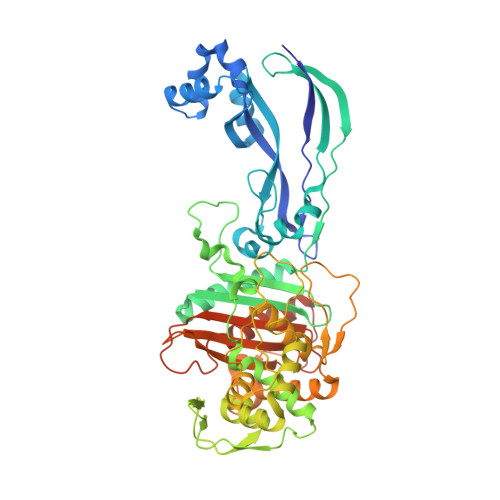
Ceftobiprole is an advanced-generation broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic with potent and rapid bactericidal activity against Gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus , as well as susceptible Gram-negative pathogens, including Pseudomonas sp. pathogens. In the case of Pseudomonas aeruginosa , ceftobiprole acts by inhibiting P. aeruginosa penicillin-binding protein 3 (PBP3). Structural studies were pursued to elucidate the molecular details of this PBP inhibition. The crystal structure of the His-tagged PBP3-ceftobiprole complex revealed a covalent bond between the ligand and the catalytic residue S294. Ceftobiprole binding leads to large active site changes near binding sites for the pyrrolidinone and pyrrolidine rings. The S528 to L536 region adopts a conformation previously not observed in PBP3, including partial unwinding of the α11 helix. These molecular insights can lead to a deeper understanding of β-lactam-PBP interactions that result in major changes in protein structure, as well as suggesting how to fine-tune current inhibitors and to develop novel inhibitors of this PBP.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, USA.