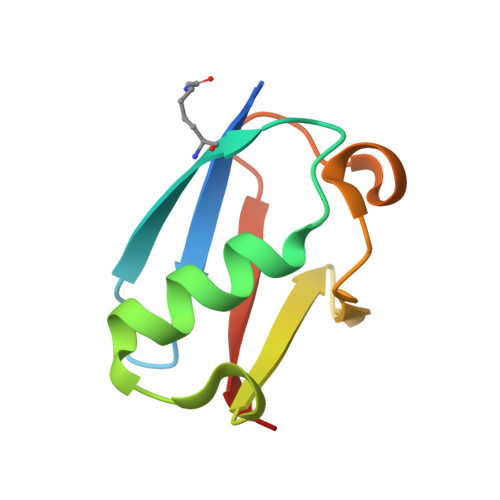
Characterization of a C-Terminal SUMO-Interacting Motif Present in Select PIAS-Family Proteins.
Lussier-Price, M., Mascle, X.H., Cappadocia, L., Kamada, R., Sakaguchi, K., Wahba, H.M., Omichinski, J.G.(2020) Structure 28: 573-585.e5
- PubMed: 32348746
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.04.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V7P, 6V7Q, 6V7R, 6V7S - PubMed Abstract:
The human PIAS proteins are small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) E3 ligases that participate in important cellular functions. Several of these functions depend on a conserved SUMO-interacting motif (SIM) located in the central region of all PIAS proteins (SIM1). Recently, it was determined that Siz2, a yeast homolog of PIAS proteins, possesses a second SIM at its C terminus (SIM2). Sequence alignment indicates that a SIM2 is also present in PIAS1-3, but not PIAS4. Using biochemical and structural studies, we demonstrate PIAS-SIM2 binds to SUMO1, but that phosphorylation of the PIAS-SIM2 or acetylation of SUMO1 alter this interaction in a manner distinct from what is observed for the PIAS-SIM1. We also show that the PIAS-SIM2 plays a key role in formation of a UBC9-PIAS1-SUMO1 complex. These results provide insights into how post-translational modifications selectively regulate the specificity of multiple SIMs found in the PIAS proteins by exploiting the plasticity built into the SUMO-SIM binding interface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Département de Biochimie et Médicine Moléculaire, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128 Succursale Centre-Ville, Montréal, QC H3C 3J7, Canada.