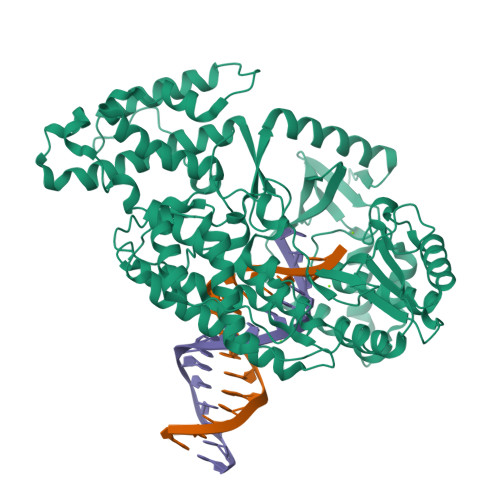
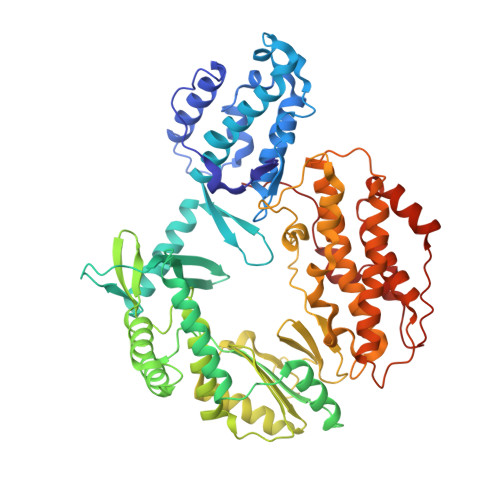
Mechanisms of nucleotide selection by telomerase.
Schaich, M.A., Sanford, S.L., Welfer, G.A., Johnson, S.A., Khoang, T.H., Opresko, P.L., Freudenthal, B.D.(2020) Elife 9
- PubMed: 32501800
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.55438
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6USO, 6USP, 6USQ, 6USR - PubMed Abstract:
Telomerase extends telomere sequences at chromosomal ends to protect genomic DNA. During this process it must select the correct nucleotide from a pool of nucleotides with various sugars and base pairing properties, which is critically important for the proper capping of telomeric sequences by shelterin. Unfortunately, how telomerase selects correct nucleotides is unknown. Here, we determined structures of Tribolium castaneum telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) throughout its catalytic cycle and mapped the active site residues responsible for nucleoside selection, metal coordination, triphosphate binding, and RNA template stabilization. We found that TERT inserts a mismatch or ribonucleotide ~1 in 10,000 and ~1 in 14,000 insertion events, respectively. At biological ribonucleotide concentrations, these rates translate to ~40 ribonucleotides inserted per 10 kilobases. Human telomerase assays determined a conserved tyrosine steric gate regulates ribonucleotide insertion into telomeres. Cumulatively, our work provides insight into how telomerase selects the proper nucleotide to maintain telomere integrity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, United States.