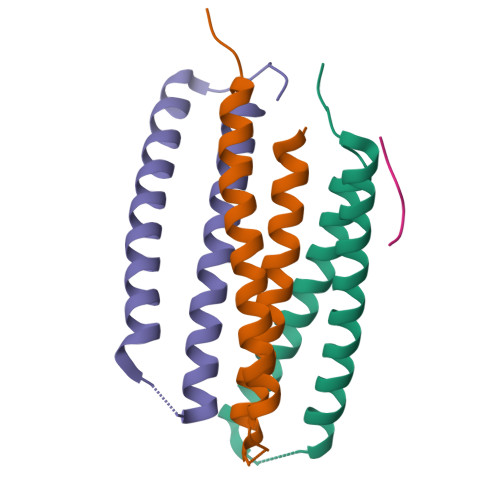
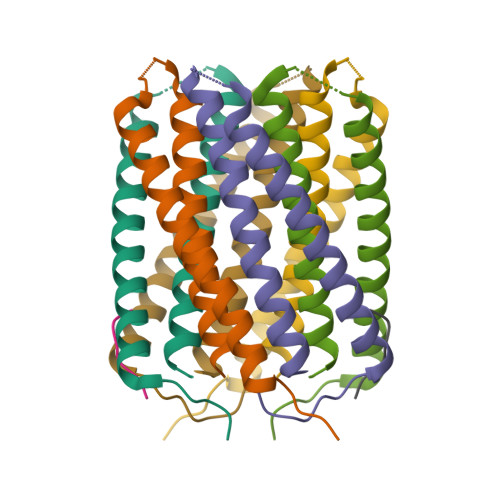
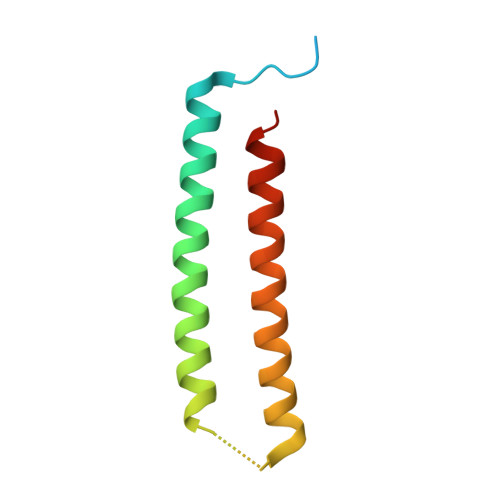
Computational design of transmembrane pores.
Xu, C., Lu, P., Gamal El-Din, T.M., Pei, X.Y., Johnson, M.C., Uyeda, A., Bick, M.J., Xu, Q., Jiang, D., Bai, H., Reggiano, G., Hsia, Y., Brunette, T.J., Dou, J., Ma, D., Lynch, E.M., Boyken, S.E., Huang, P.S., Stewart, L., DiMaio, F., Kollman, J.M., Luisi, B.F., Matsuura, T., Catterall, W.A., Baker, D.(2020) Nature 585: 129-134
- PubMed: 32848250
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2646-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6M6Z, 6O35, 6TJ1, 6TMS - PubMed Abstract:
Transmembrane channels and pores have key roles in fundamental biological processes 1 and in biotechnological applications such as DNA nanopore sequencing 2-4 , resulting in considerable interest in the design of pore-containing proteins. Synthetic amphiphilic peptides have been found to form ion channels 5,6 , and there have been recent advances in de novo membrane protein design 7,8 and in redesigning naturally occurring channel-containing proteins 9,10 . However, the de novo design of stable, well-defined transmembrane protein pores that are capable of conducting ions selectively or are large enough to enable the passage of small-molecule fluorophores remains an outstanding challenge 11,12 . Here we report the computational design of protein pores formed by two concentric rings of α-helices that are stable and monodisperse in both their water-soluble and their transmembrane forms. Crystal structures of the water-soluble forms of a 12-helical pore and a 16-helical pore closely match the computational design models. Patch-clamp electrophysiology experiments show that, when expressed in insect cells, the transmembrane form of the 12-helix pore enables the passage of ions across the membrane with high selectivity for potassium over sodium; ion passage is blocked by specific chemical modification at the pore entrance. When incorporated into liposomes using in vitro protein synthesis, the transmembrane form of the 16-helix pore-but not the 12-helix pore-enables the passage of biotinylated Alexa Fluor 488. A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the 16-helix transmembrane pore closely matches the design model. The ability to produce structurally and functionally well-defined transmembrane pores opens the door to the creation of designer channels and pores for a wide variety of applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Protein Design, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.