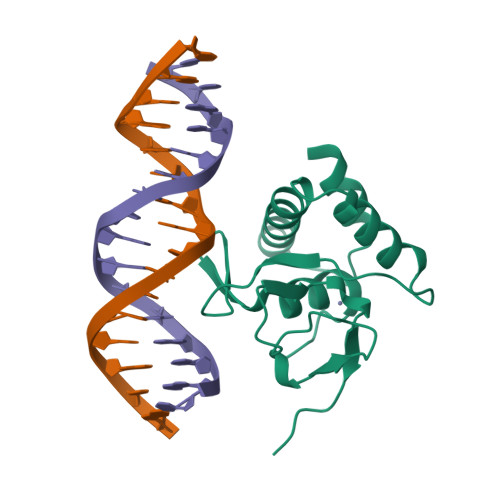
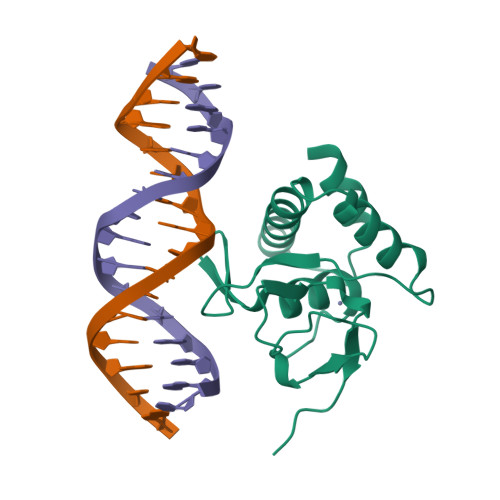
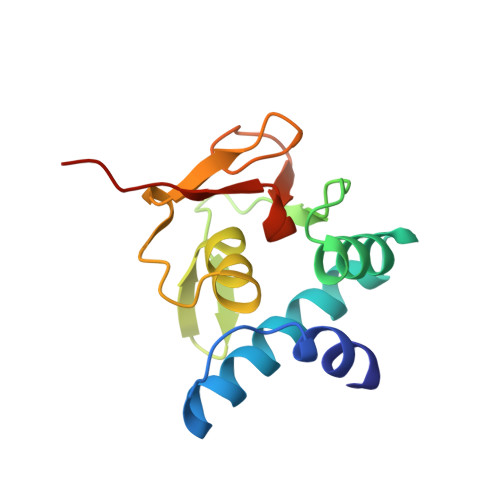
Unveiling the dimer/monomer propensities of Smad MH1-DNA complexes.
Ruiz, L., Kaczmarska, Z., Gomes, T., Aragon, E., Torner, C., Freier, R., Baginski, B., Martin-Malpartida, P., de Martin Garrido, N., Marquez, J.A., Cordeiro, T.N., Pluta, R., Macias, M.J.(2021) Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19: 632-646
- PubMed: 33510867
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6TBZ, 6TCE, 6ZMN - PubMed Abstract:
Smad transcription factors are the main downstream effectors of the Transforming growth factor β superfamily (TGFβ) signalling network. The DNA complexes determined here by X-ray crystallography for the Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP) activated Smad5 and Smad8 proteins reveal that all MH1 domains bind [GGC(GC)|(CG)] motifs similarly, although TGFβ-activated Smad2/3 and Smad4 MH1 domains bind as monomers whereas Smad1/5/8 form helix-swapped dimers. Dimers and monomers are also present in solution, as revealed by NMR. To decipher the characteristics that defined these dimers, we designed chimeric MH1 domains and characterized them using X-ray crystallography. We found that swapping the loop1 between TGFβ- and BMP- activated MH1 domains switches the dimer/monomer propensities. When we scanned the distribution of Smad-bound motifs in ChIP-Seq peaks (Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing) in Smad-responsive genes, we observed specific site clustering and spacing depending on whether the peaks correspond to BMP- or TGFβ-responsive genes. We also identified significant correlations between site distribution and monomer or dimer propensities. We propose that the MH1 monomer or dimer propensity of Smads contributes to the distinct motif selection genome-wide and together with the MH2 domain association, help define the composition of R-Smad/Smad4 trimeric complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Research in Biomedicine, The Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, Baldiri Reixac, 10, Barcelona 08028, Spain.