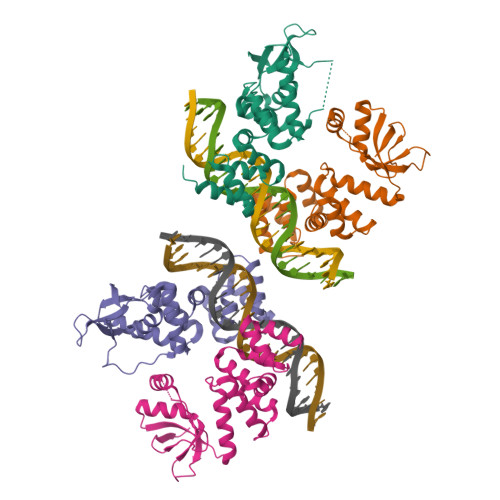
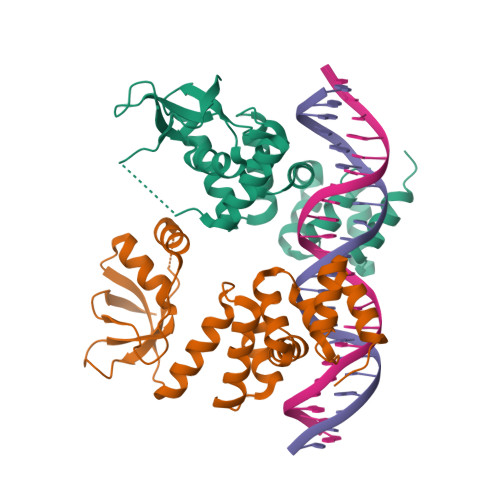
A CTP-dependent gating mechanism enables ParB spreading on DNA.
Jalal, A.S., Tran, N.T., Stevenson, C.E., Chimthanawala, A., Badrinarayanan, A., Lawson, D.M., Le, T.B.(2021) Elife 10
- PubMed: 34397383
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.69676
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6T1F, 7BM8 - PubMed Abstract:
Proper chromosome segregation is essential in all living organisms. The ParA-ParB- parS system is widely employed for chromosome segregation in bacteria. Previously, we showed that Caulobacter crescentus ParB requires cytidine triphosphate to escape the nucleation site parS and spread by sliding to the neighboring DNA (Jalal et al., 2020). Here, we provide the structural basis for this transition from nucleation to spreading by solving co-crystal structures of a C-terminal domain truncated C. crescentus ParB with parS and with a CTP analog. Nucleating ParB is an open clamp, in which parS is captured at the DNA-binding domain (the DNA-gate). Upon binding CTP, the N-terminal domain (NTD) self-dimerizes to close the NTD-gate of the clamp. The DNA-gate also closes, thus driving parS into a compartment between the DNA-gate and the C-terminal domain. CTP hydrolysis and/or the release of hydrolytic products are likely associated with reopening of the gates to release DNA and recycle ParB. Overall, we suggest a CTP-operated gating mechanism that regulates ParB nucleation, spreading, and recycling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Microbiology, John Innes Centre, Norwich, United Kingdom.