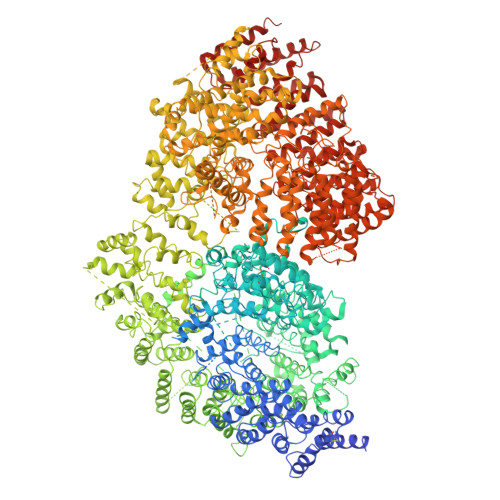
The Polyglutamine Expansion at the N-Terminal of Huntingtin Protein Modulates the Dynamic Configuration and Phosphorylation of the C-Terminal HEAT Domain.
Jung, T., Shin, B., Tamo, G., Kim, H., Vijayvargia, R., Leitner, A., Marcaida, M.J., Astorga-Wells, J., Jung, R., Aebersold, R., Peraro, M.D., Hebert, H., Seong, I.S., Song, J.J.(2020) Structure 28: 1035-1050.e8
- PubMed: 32668197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.06.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RMH, 6YEJ - PubMed Abstract:
The polyQ expansion in huntingtin protein (HTT) is the prime cause of Huntington's disease (HD). The recent cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of HTT-HAP40 complex provided the structural information on its HEAT-repeat domains. Here, we present analyses of the impact of polyQ length on the structure and function of HTT via an integrative structural and biochemical approach. The cryo-EM analysis of normal (Q23) and disease (Q78) type HTTs shows that the structures of apo HTTs significantly differ from the structure of HTT in a HAP40 complex and that the polyQ expansion induces global structural changes in the relative movements among the HTT domains. In addition, we show that the polyQ expansion alters the phosphorylation pattern across HTT and that Ser2116 phosphorylation in turn affects the global structure and function of HTT. These results provide a molecular basis for the effect of the polyQ segment on HTT structure and activity, which may be important for HTT pathology.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), KI for the BioCentury, Daejeon 34141, Korea; School of Engineering Sciences in Chemistry, Biotechnology and Health, Department of Biomedical Engineering and Health Systems, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, 141 52 Huddinge, Sweden; Department of Biosciences and Nutrition, Karolinska Institutet, 141 83 Huddinge, Sweden.