A molecular mechanism for LINC complex branching by structurally diverse SUN-KASH 6:6 assemblies.
Gurusaran, M., Davies, O.R.(2021) Elife 10
- PubMed: 33393904
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60175
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6R15, 6R16, 6R2I - PubMed Abstract:
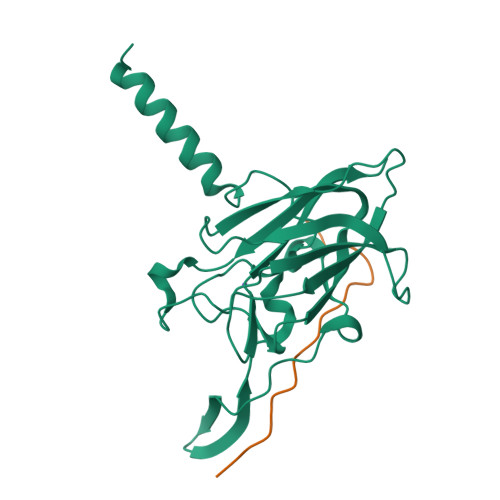
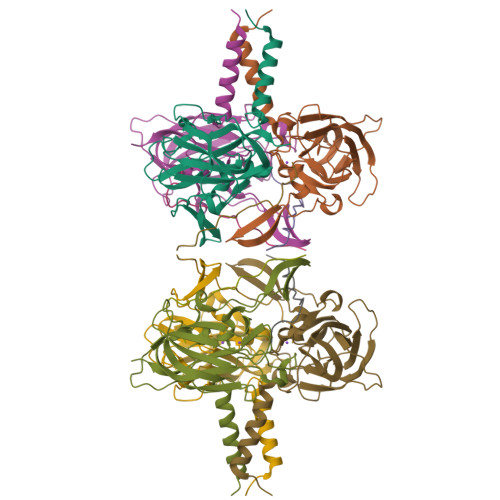
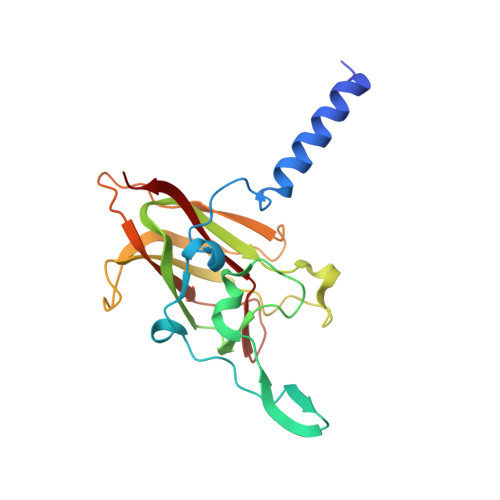
The Linker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton (LINC) complex mechanically couples cytoskeletal and nuclear components across the nuclear envelope to fulfil a myriad of cellular functions, including nuclear shape and positioning, hearing, and meiotic chromosome movements. The canonical model is that 3:3 interactions between SUN and KASH proteins underlie the nucleocytoskeletal linkages provided by the LINC complex. Here, we provide crystallographic and biophysical evidence that SUN-KASH is a constitutive 6:6 complex in which two constituent 3:3 complexes interact head-to-head. A common SUN-KASH topology is achieved through structurally diverse 6:6 interaction mechanisms by distinct KASH proteins, including zinc-coordination by Nesprin-4. The SUN-KASH 6:6 interface provides a molecular mechanism for the establishment of integrative and distributive connections between 3:3 structures within a branched LINC complex network. In this model, SUN-KASH 6:6 complexes act as nodes for force distribution and integration between adjacent SUN and KASH molecules, enabling the coordinated transduction of large forces across the nuclear envelope.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Cell Biology, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.