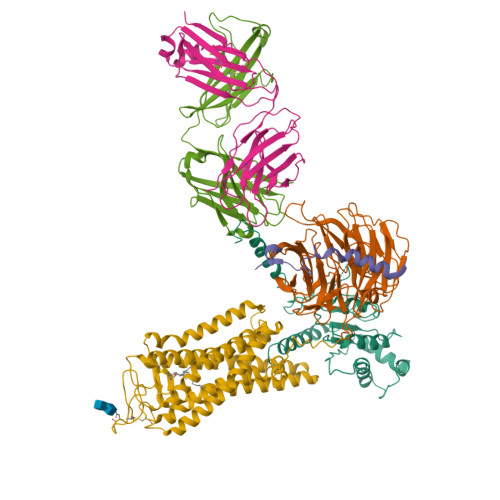
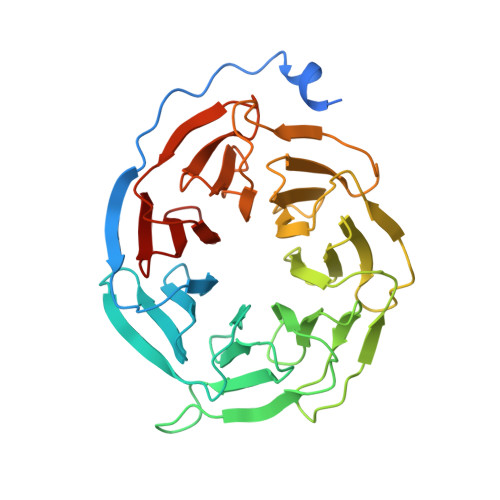
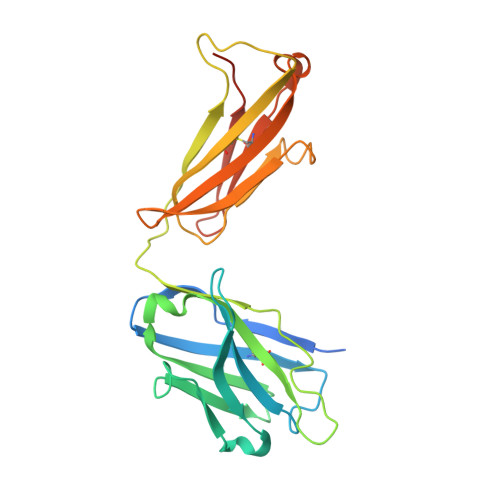
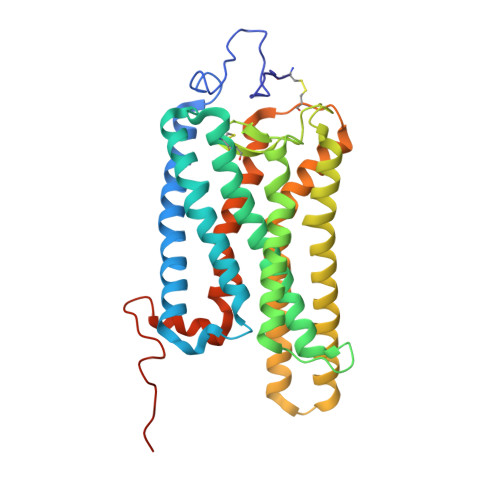
Cryo-EM structure of the rhodopsin-G alpha i-beta gamma complex reveals binding of the rhodopsin C-terminal tail to the G beta subunit.
Tsai, C.J., Marino, J., Adaixo, R., Pamula, F., Muehle, J., Maeda, S., Flock, T., Taylor, N.M., Mohammed, I., Matile, H., Dawson, R.J., Deupi, X., Stahlberg, H., Schertler, G.(2019) Elife 8
- PubMed: 31251171
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6QNK, 6QNO - PubMed Abstract:
One of the largest membrane protein families in eukaryotes are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs modulate cell physiology by activating diverse intracellular transducers, prominently heterotrimeric G proteins. The recent surge in structural data has expanded our understanding of GPCR-mediated signal transduction. However, many aspects, including the existence of transient interactions, remain elusive. We present the cryo-EM structure of the light-sensitive GPCR rhodopsin in complex with heterotrimeric Gi. Our density map reveals the receptor C-terminal tail bound to the Gβ subunit of the G protein, providing a structural foundation for the role of the C-terminal tail in GPCR signaling, and of Gβ as scaffold for recruiting Gα subunits and G protein-receptor kinases. By comparing available complexes, we found a small set of common anchoring points that are G protein-subtype specific. Taken together, our structure and analysis provide new structural basis for the molecular events of the GPCR signaling pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biology and Chemistry / Laboratory of Biomolecular Research, Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen, Switzerland.