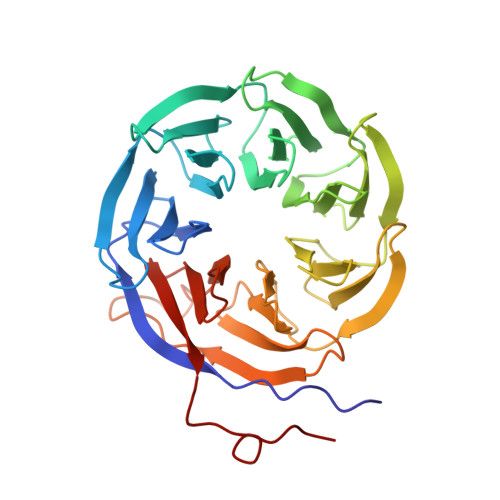
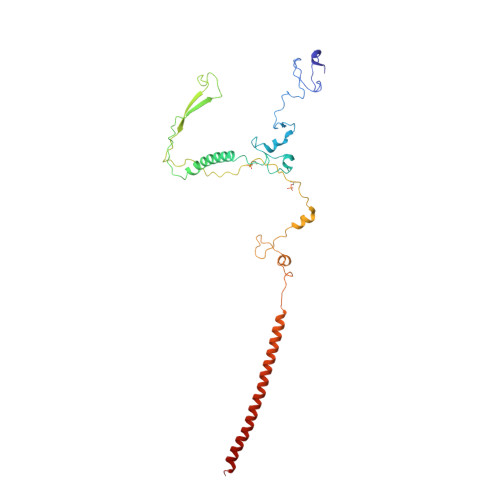
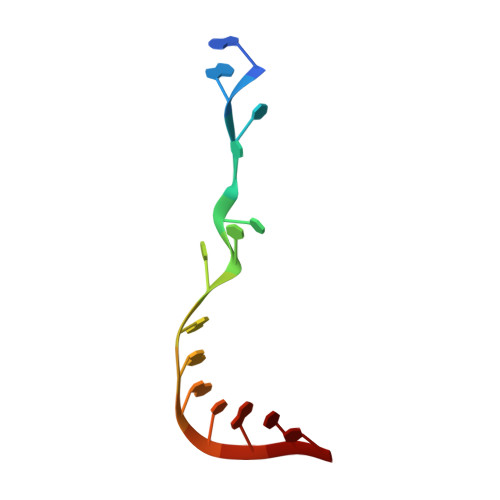
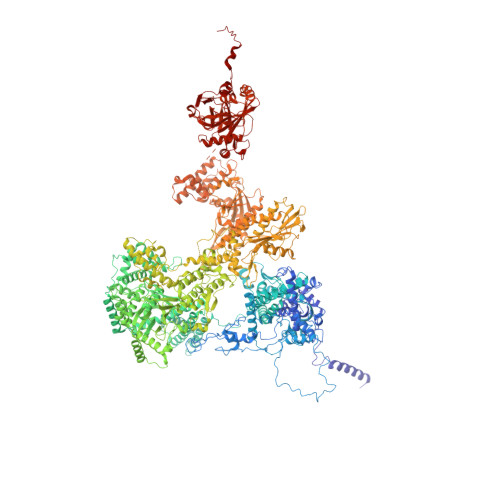
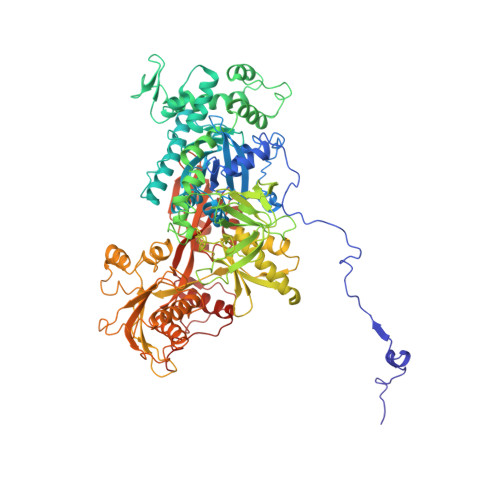
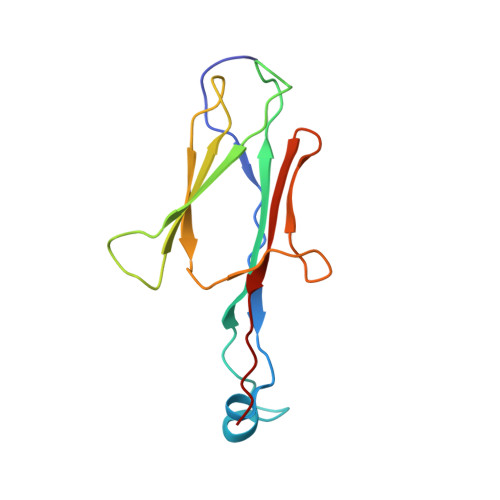
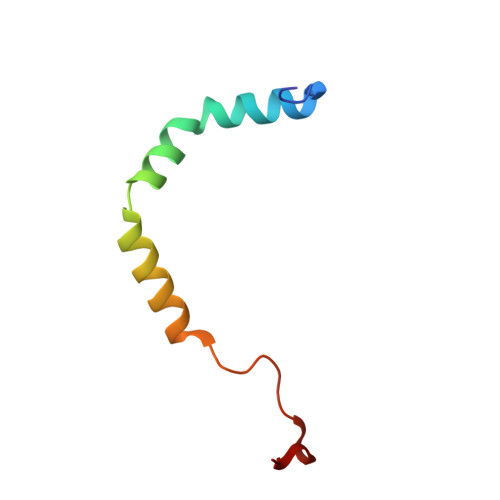
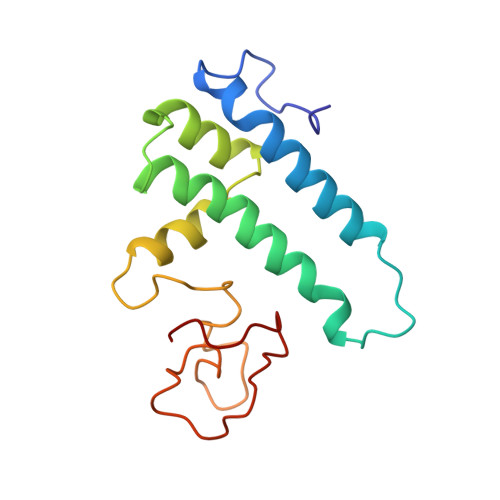
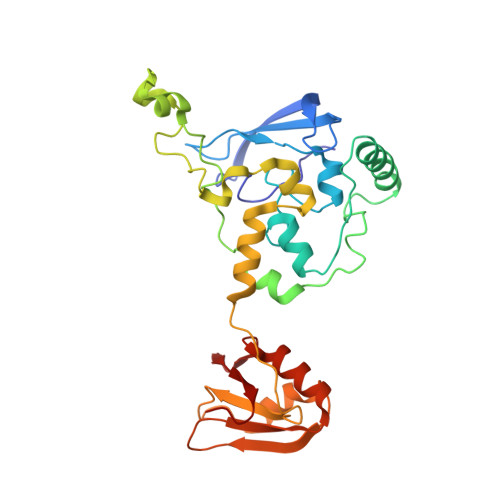
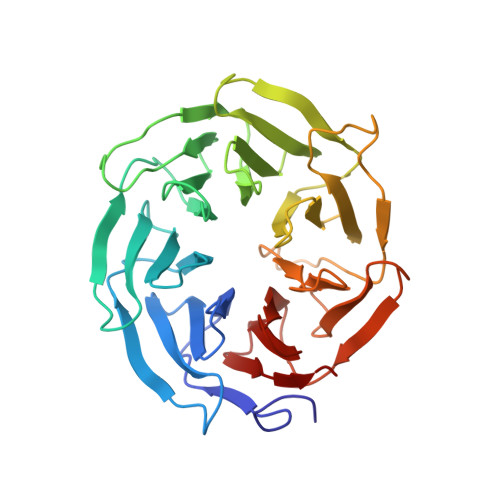
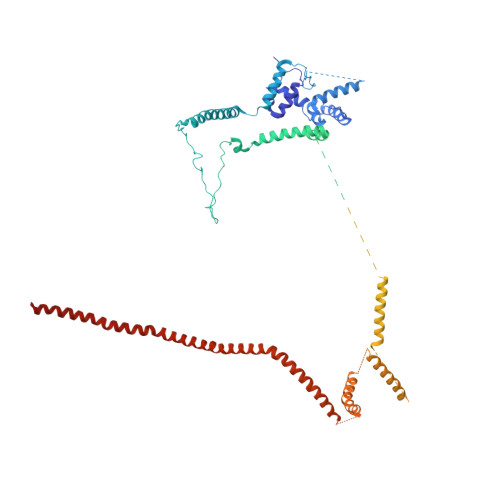
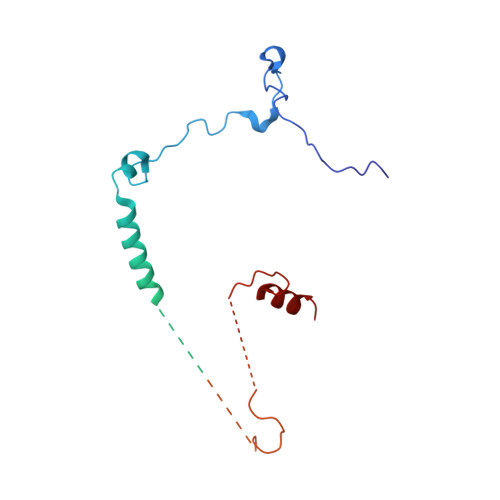
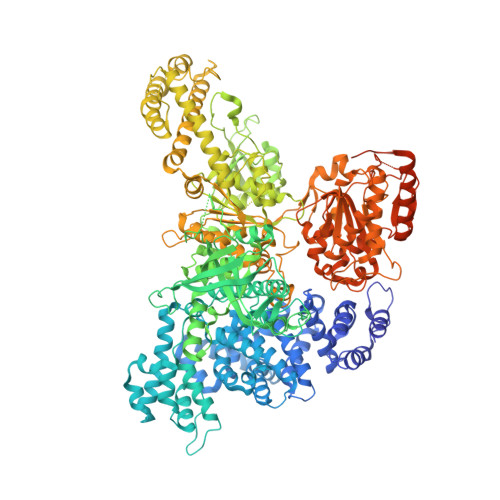
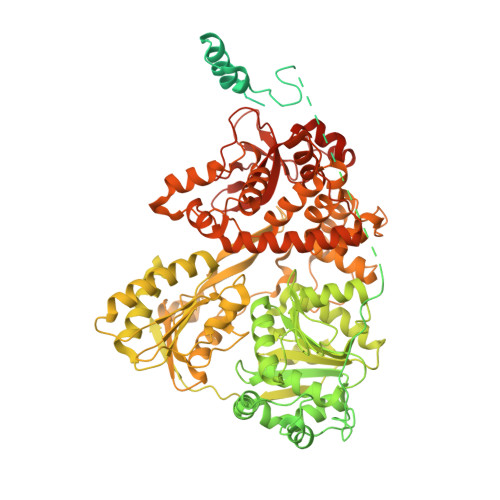
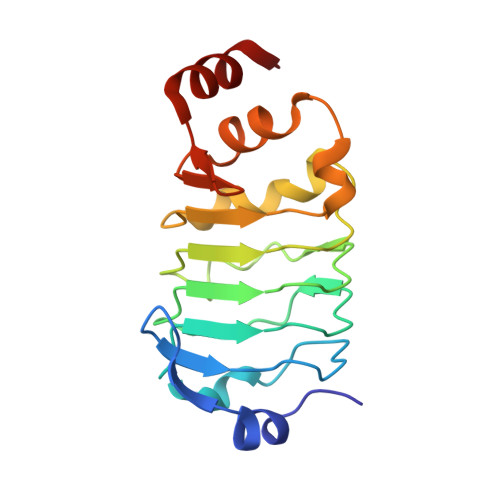
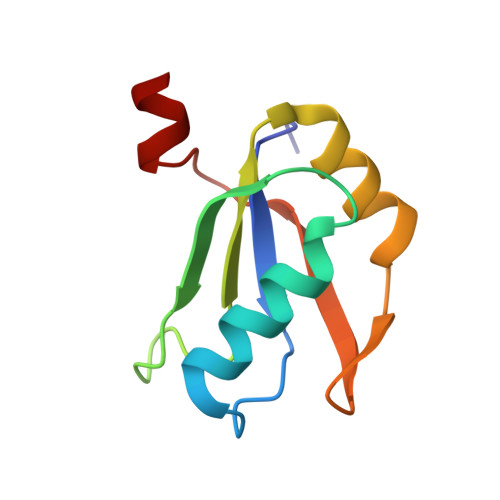
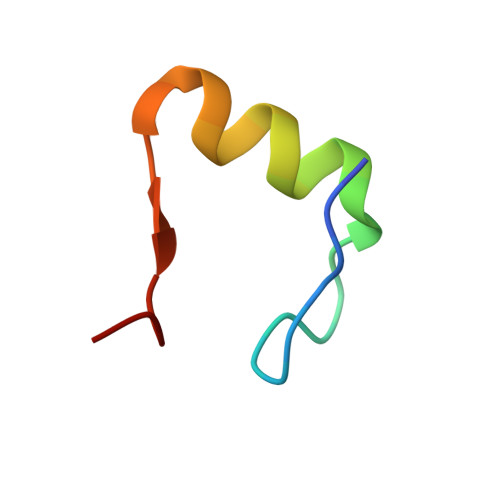
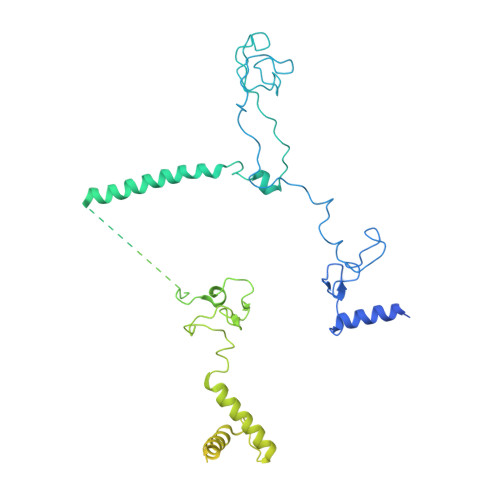
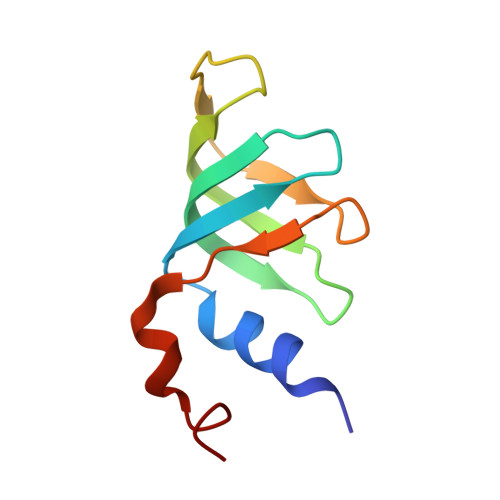
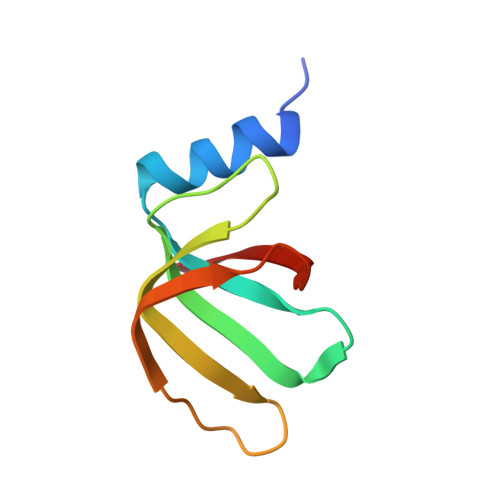
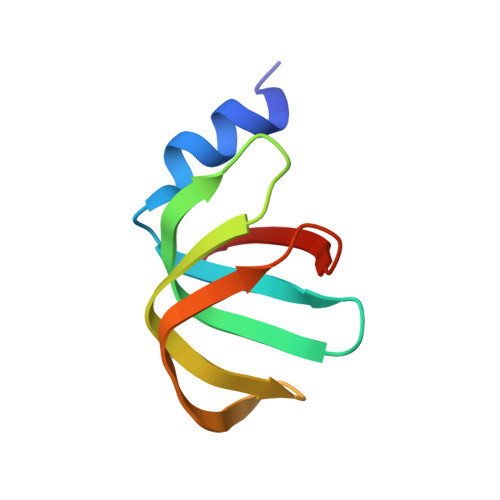
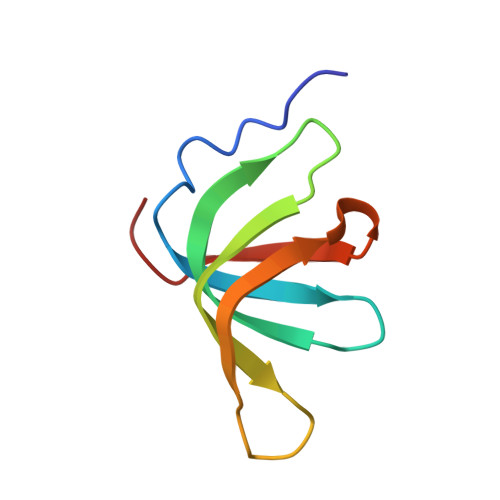
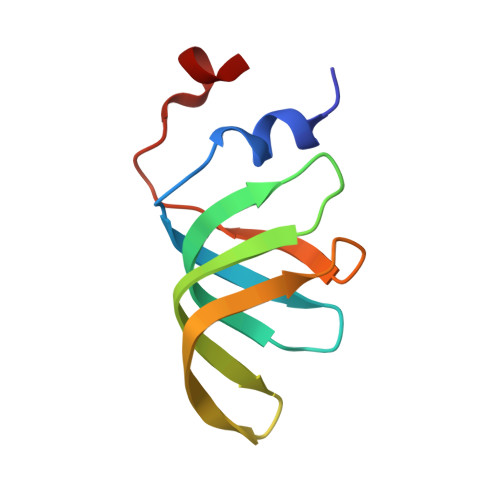
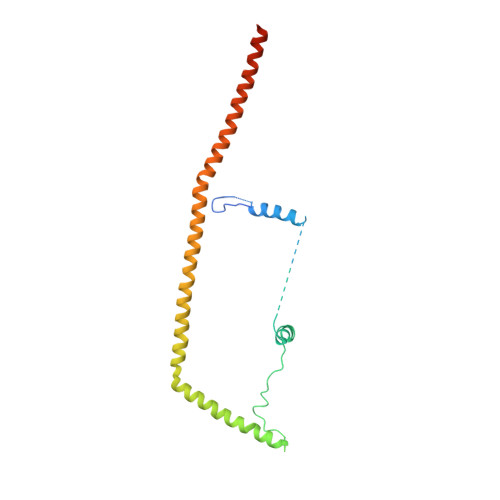
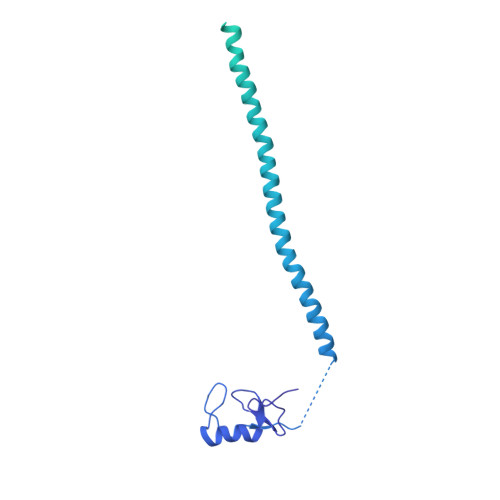
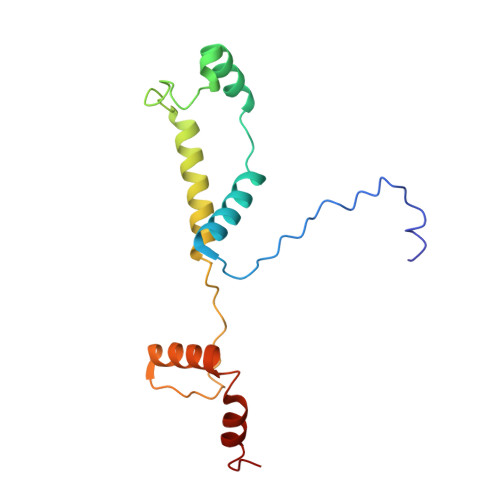
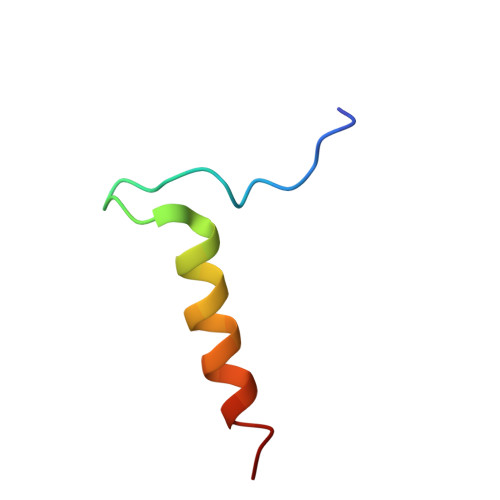
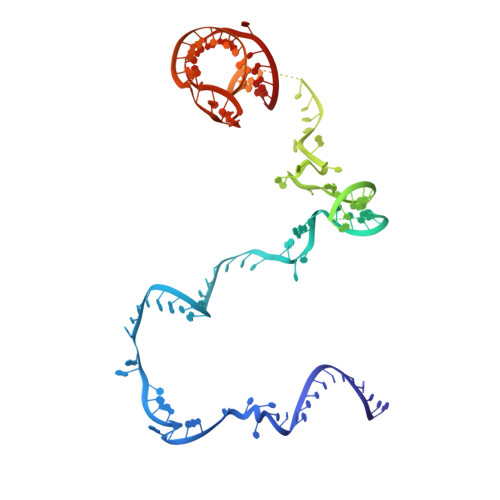
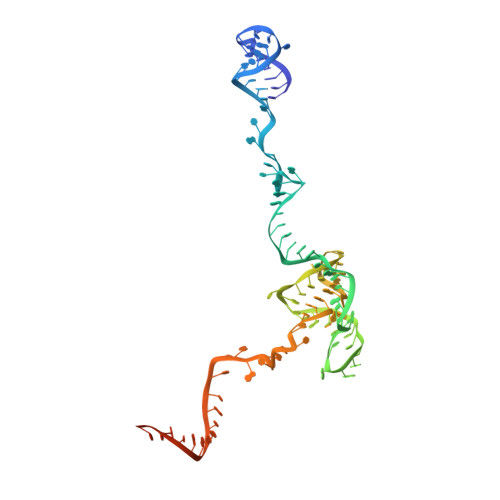
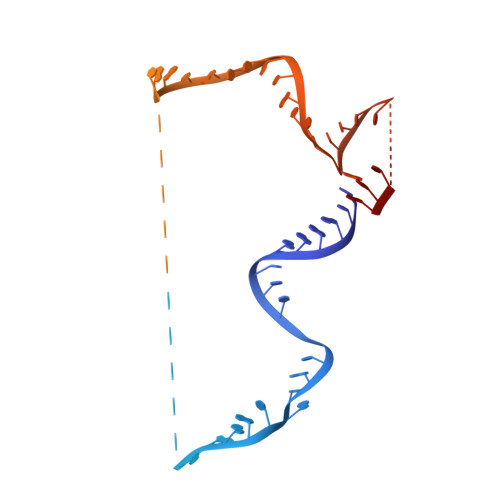
A human postcatalytic spliceosome structure reveals essential roles of metazoan factors for exon ligation.
Fica, S.M., Oubridge, C., Wilkinson, M.E., Newman, A.J., Nagai, K.(2019) Science 363: 710-714
- PubMed: 30705154
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaw5569
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6QDV - PubMed Abstract:
During exon ligation, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spliceosome recognizes the 3'-splice site (3'SS) of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) through non-Watson-Crick pairing with the 5'SS and the branch adenosine, in a conformation stabilized by Prp18 and Prp8. Here we present the 3.3-angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of a human postcatalytic spliceosome just after exon ligation. The 3'SS docks at the active site through conserved RNA interactions in the absence of Prp18. Unexpectedly, the metazoan-specific FAM32A directly bridges the 5'-exon and intron 3'SS of pre-mRNA and promotes exon ligation, as shown by functional assays. CACTIN, SDE2, and NKAP-factors implicated in alternative splicing-further stabilize the catalytic conformation of the spliceosome during exon ligation. Together these four proteins act as exon ligation factors. Our study reveals how the human spliceosome has co-opted additional proteins to modulate a conserved RNA-based mechanism for 3'SS selection and to potentially fine-tune alternative splicing at the exon ligation stage.
- MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK. sfica@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk kn@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk.
Organizational Affiliation: