Crystal Structure of the Carbohydrate Recognition Domain of the Human Macrophage Galactose C-Type Lectin Bound to GalNAc and the Tumor-Associated Tn Antigen.
Gabba, A., Bogucka, A., Luz, J.G., Diniz, A., Coelho, H., Corzana, F., Canada, F.J., Marcelo, F., Murphy, P.V., Birrane, G.(2021) Biochemistry 60: 1327-1336
- PubMed: 33724805
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PUV, 6PY1, 6W12, 6XIY - PubMed Abstract:
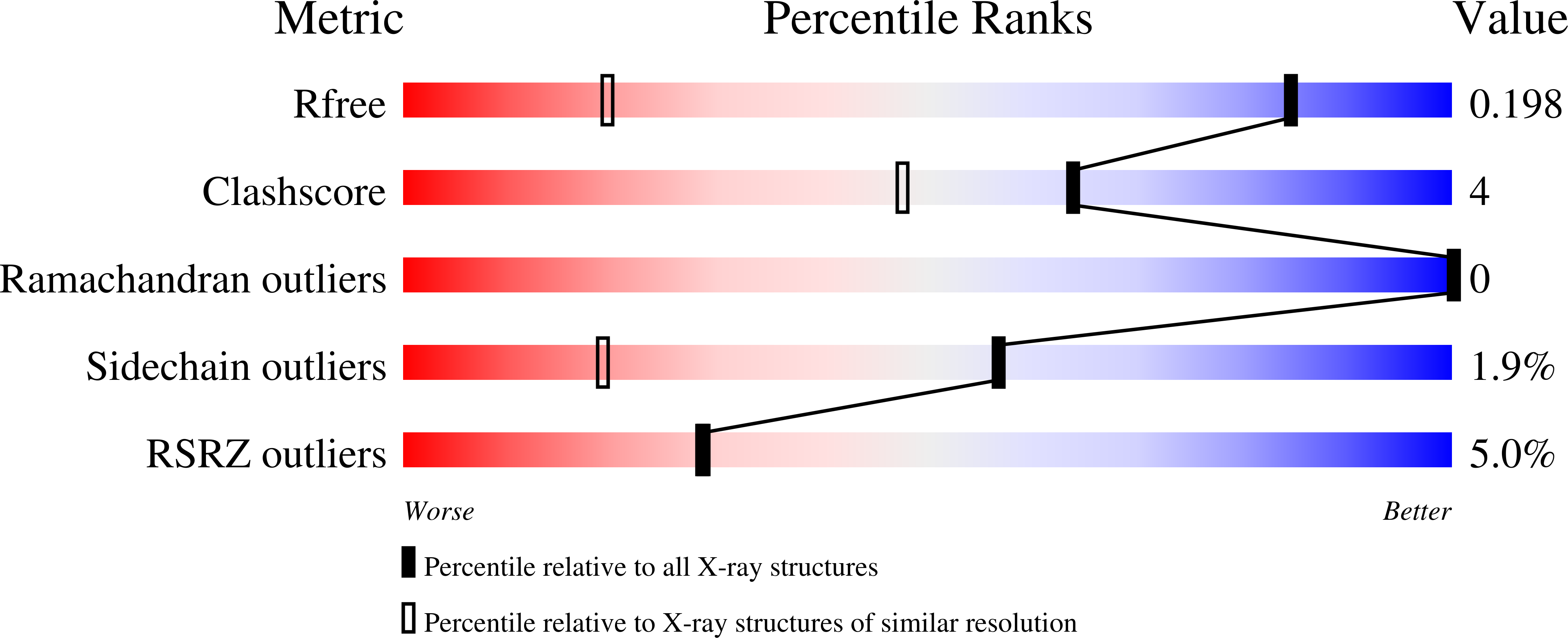
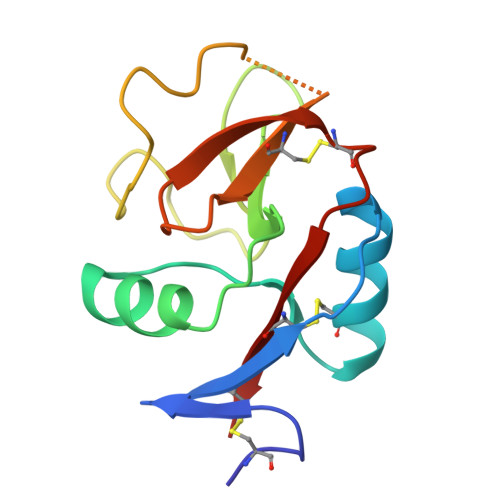
The human macrophage galactose lectin (MGL) is an endocytic type II transmembrane receptor expressed on immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells and activated macrophages and plays a role in modulating the immune system in response to infections and cancer. MGL contains an extracellular calcium-dependent (C-type) carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) that specifically binds terminal N- acetylgalactosamine glycan residues such as the Tn and sialyl-Tn antigens found on tumor cells, as well as other N- and O- glycans displayed on certain viruses and parasites. Even though the glycan specificity of MGL is known and several binding glycoproteins have been identified, the molecular basis for substrate recognition has remained elusive due to the lack of high-resolution structures. Here we present crystal structures of the MGL CRD at near endosomal pH and in several complexes, which reveal details of the interactions with the natural ligand, GalNAc, the cancer-associated Tn-Ser antigen, and a synthetic GalNAc mimetic ligand. Like the asialoglycoprotein receptor, additional calcium atoms are present and contribute to stabilization of the MGL CRD fold. The structure provides the molecular basis for preferential binding of N- acetylgalactosamine over galactose and prompted the re-evaluation of the binding modes previously proposed in solution. Saturation transfer difference nuclear magnetic resonance data acquired using the MGL CRD and interpreted using the crystal structure indicate a single binding mode for GalNAc in solution. Models of MGL1 and MGL2, the mouse homologues of MGL, explain how these proteins might recognize Lewis X and GalNAc, respectively.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Experimental Medicine, Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02215, United States.