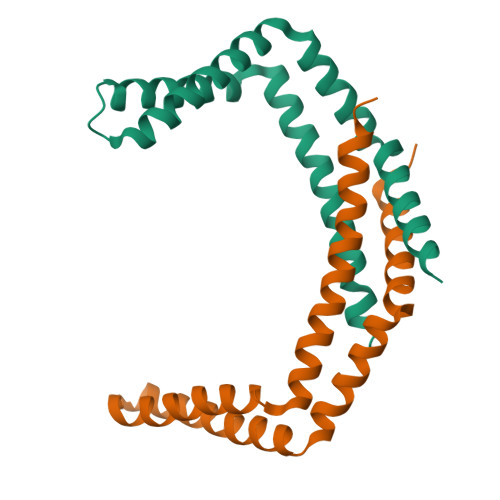
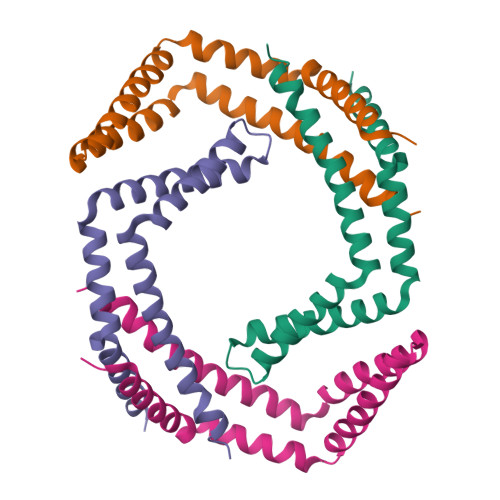
Structure-Function Studies of the Bacillus subtilis Ric Proteins Identify the Fe-S Cluster-Ligating Residues and Their Roles in Development and RNA Processing.
Adusei-Danso, F., Khaja, F.T., DeSantis, M., Jeffrey, P.D., Dubnau, E., Demeler, B., Neiditch, M.B., Dubnau, D.(2019) mBio 10
- PubMed: 31530674
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01841-19
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PRH, 6PRK - PubMed Abstract:
In Bacillus subtilis , the RicA (YmcA), RicF (YlbF), and RicT (YaaT) proteins accelerate the phosphorylation of the transcription factor Spo0A, contributing to genetic competence, sporulation, and biofilm formation, and are also essential for the correct maturation of several protein-encoding and riboswitch RNAs. These proteins form a stable complex (RicAFT) that carries two [4Fe-4S] +2 clusters. We show here that the complex is a 1:1:1 heterotrimer, and we present the X-ray crystal structures of a RicAF heterotetramer and of a RicA dimer. We also demonstrate that one of the Fe-S clusters (cluster 1) is ligated by cysteine residues donated exclusively by RicT and can be retained when the RicT monomer is purified by itself. Cluster 2 is ligated by C167 from RicT, by C134 and C146 located near the C terminus of RicF, and by C141 at the C terminus of RicA. These findings imply the following novel arrangement: adjacent RicT residues C166 and 167 ligate clusters 1 and 2, respectively, while cluster 2 is ligated by cysteine residues from RicT, RicA, and RicF. Thus, the two clusters must lie close to one another and at the interface of the RicAFT protomers. We also show that the cluster-ligating cysteine residues, and therefore most likely both Fe-S clusters, are essential for cggR-gapA mRNA maturation, for the regulation of ricF transcript stability, and for several Ric-associated developmental phenotypes, including competence for transformation, biofilm formation, and sporulation. Finally, we present evidence that RicAFT, RicAF, and RicA and the RicT monomer may play distinct regulatory roles in vivo IMPORTANCE The RicA, RicF, and RicT proteins are widely conserved among the firmicute bacteria and play multiple roles in Bacillus subtilis Among the phenotypes associated with the inactivation of these proteins are the inability to be genetically transformed or to form biofilms, a decrease in sporulation frequency, and changes in the stability and maturation of multiple RNA species. Despite their importance, the molecular mechanisms of Ric protein activities have not been elucidated and the roles of the two iron-sulfur clusters on the complex of the three proteins are not understood. To unravel the mechanisms of Ric action, molecular characterization of the complex and of its constituent proteins is essential. This report represents a major step toward understanding the structures of the Ric proteins, the arrangement and roles of the Fe-S clusters, and the phenotypes associated with Ric mutations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, New Jersey Medical School, Rutgers University, Newark, New Jersey, USA.