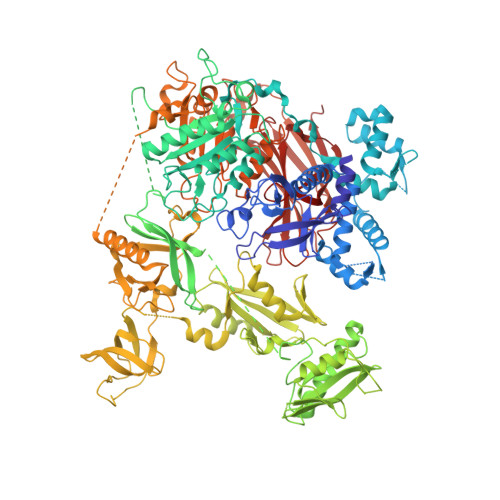
Structural basis for the activation of PLC-gamma isozymes by phosphorylation and cancer-associated mutations.
Hajicek, N., Keith, N.C., Siraliev-Perez, E., Temple, B.R.S., Huang, W., Zhang, Q., Harden, T.K., Sondek, J.(2019) Elife 8
- PubMed: 31889510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.51700
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6PBC - PubMed Abstract:
Direct activation of the human phospholipase C-γ isozymes (PLC-γ1, -γ2) by tyrosine phosphorylation is fundamental to the control of diverse biological processes, including chemotaxis, platelet aggregation, and adaptive immunity. In turn, aberrant activation of PLC-γ1 and PLC-γ2 is implicated in inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Although structures of isolated domains from PLC-γ isozymes are available, these structures are insufficient to define how release of basal autoinhibition is coupled to phosphorylation-dependent enzyme activation. Here, we describe the first high-resolution structure of a full-length PLC-γ isozyme and use it to underpin a detailed model of their membrane-dependent regulation. Notably, an interlinked set of regulatory domains integrates basal autoinhibition, tyrosine kinase engagement, and additional scaffolding functions with the phosphorylation-dependent, allosteric control of phospholipase activation. The model also explains why mutant forms of the PLC-γ isozymes found in several cancers have a wide spectrum of activities, and highlights how these activities are tuned during disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, United States.