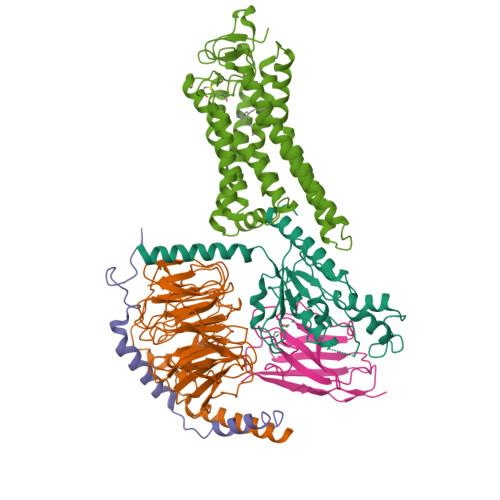
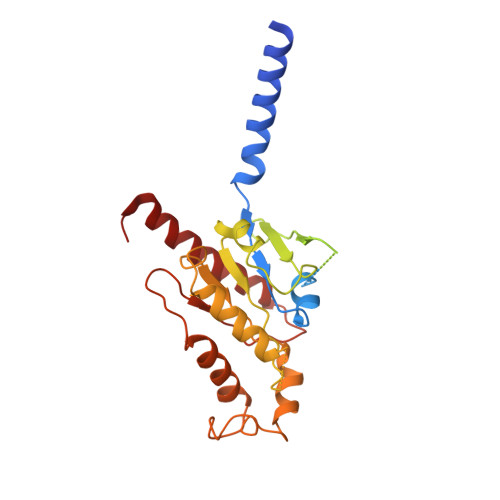
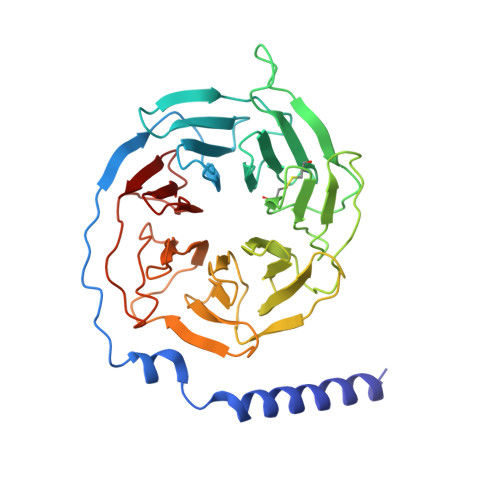
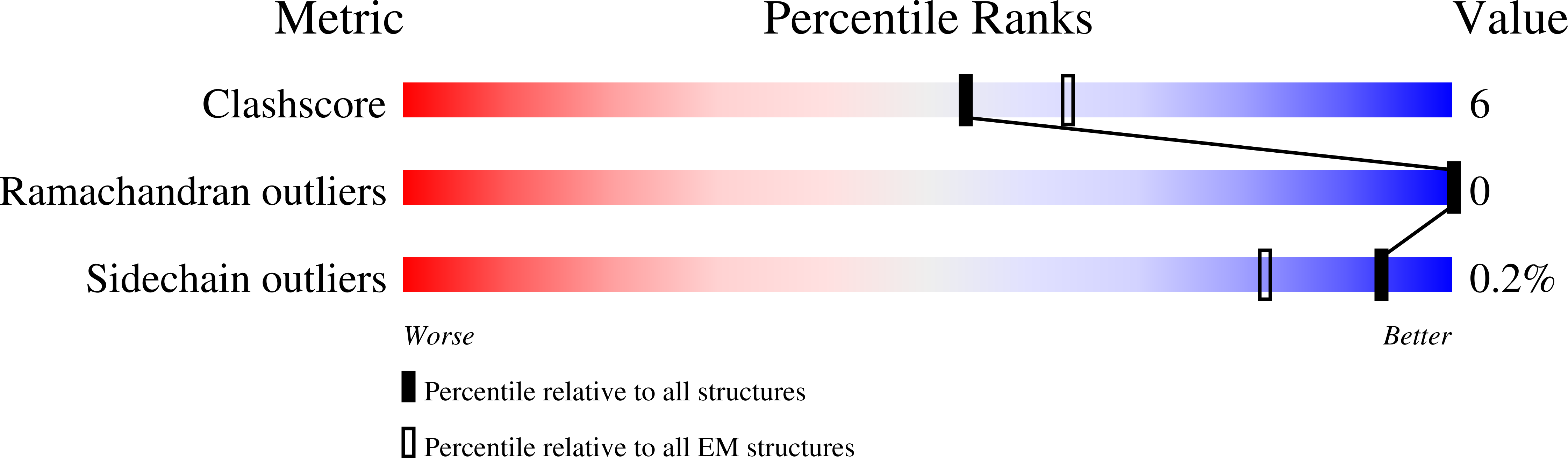Structures of the Rhodopsin-Transducin Complex: Insights into G-Protein Activation.
Gao, Y., Hu, H., Ramachandran, S., Erickson, J.W., Cerione, R.A., Skiniotis, G.(2019) Mol Cell 75: 781
- PubMed: 31300275
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OY9, 6OYA - PubMed Abstract:
Rhodopsin (Rho), a prototypical G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) in vertebrate vision, activates the G-protein transducin (G T ) by catalyzing GDP-GTP exchange on its α subunit (Gα T ). To elucidate the determinants of G T coupling and activation, we obtained cryo-EM structures of a fully functional, light-activated Rho-G T complex in the presence and absence of a G-protein-stabilizing nanobody. The structures illustrate how G T overcomes its low basal activity by engaging activated Rho in a conformation distinct from other GPCR-G-protein complexes. Moreover, the nanobody-free structures reveal native conformations of G-protein components and capture three distinct conformers showing the Gα T helical domain (αHD) contacting the Gβγ subunits. These findings uncover the molecular underpinnings of G-protein activation by visual rhodopsin and shed new light on the role played by Gβγ during receptor-catalyzed nucleotide exchange.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA.